25 min read
AI in procurement: Applications, Challenges, and Mitigation Strategies
Explore the impact of AI in procurement and read about real-world applications, key challenges, and practical strategies to overcome them.
Traditionally, procurement has been a process weighed down by manual tasks, fragmented systems, and endless paperwork. Today, procurement is undergoing a transformation. While procurement teams have long worked to add strategic value, Artificial Intelligence (AI) amplifies their impact. Procurement AI enables teams to quickly process mountains of data, uncover hidden patterns, and automate repetitive tasks like invoice processing and supplier evaluations.
So, what does this transformation mean for businesses? And how can procurement leaders use procurement AI to address today’s inefficiencies and gain a competitive edge? Read on to explore key AI use cases in procurement, the challenges businesses face, strategies to overcome them, and the exciting opportunities AI brings for the future.
Here are the topics we’ll cover at a glance:
What is AI in procurement?
AI use cases in procurement
Types of procurement AI
Benefits of AI in Procurement
Challenges of AI in procurement
Mitigation strategies: How to address procurement AI risks and challenges
The future of AI and procurement
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI in procurement?
AI in procurement refers to applying advanced technologies that use artificial intelligence to make procurement processes faster, more efficient, and data-driven. Unlike traditional tools that often operate in isolation or rely on rigid workflows, AI connects the dots between disparate data sources, providing a more comprehensive view of procurement activities.
Procurement is often plagued with inefficiencies that, using old-school methods like Excel and mail, require time-consuming reviews to identify — rogue spending, misclassified expenses, delayed approvals, and duplicate invoices are just the tip of the iceberg. Procurement AI shines here by quickly analyzing large amounts of data to identify patterns, flag anomalies, and uncover opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
However, it’s important to remember that AI use cases in procurement aren’t about replacing human expertise: AI won’t drive organizational change or deliver savings on its own. Instead, it’s a powerful tool that requires expert guidance and oversight to truly add value.
AI use cases in procurement
Here are the key AI in procurement examples that are transforming how teams work:
Spend analysis
AI for procurement enhances spend analysis by efficiently processing and analyzing large volumes of data far beyond what manual approach can handle. Traditional spend analysis methods often involve time-consuming manual data entry or reliance on basic software tools that can miss key patterns, discrepancies, or hidden opportunities.
Procurement AI, however, uses advanced algorithms to automatically categorize spending data, identify spending trends, and flag anomalies in real time. For example, AI can spot recurring or unnecessary costs, detect maverick spending (when employees purchase outside of approved channels), and identify opportunities for cost savings based on historical spending patterns.
Supplier sourcing
Companies are increasingly using AI in sourcing and procurement to analyze supplier data and identify the best-fit suppliers based on factors like price and quality of goods or services, as well as delivery performance. AI can process large amounts of historical supplier performance data across multiple metrics, allowing procurement teams to make more informed, data-driven decisions instead of relying solely on anecdotal evidence or subjective evaluations.
While AI in procurement is still evolving when it comes to supplier negotiations, it is already used to analyze historical procurement-related data and current market trends, and even consider external factors like geopolitical risks. AI can then offer insights into potential negotiation strategies, for example identifying the best times to initiate price review or suggesting suppliers likely to offer favorable pricing or terms.
Contract analysis
AI in sourcing and procurement is transforming contract management by automating key tasks like contract review, compliance tracking, and renewal alerts. AI can quickly scan contracts, flagging any areas that may need attention — such as clauses that deviate from standard terms or compliance issues. AI can also track key milestones, ensuring that renewals or renegotiations happen on time and minimizing the risk of missed opportunities or penalties.
However, relying solely on generative AI in procurement for legal or contractual tasks does come with risks. While AI can flag issues, it may not fully understand the context or nuances behind legal terms. Therefore, even though AI for procurement can speed up contract management, human conrol remains essential to properly address all legal aspects.
Demand forecasting
Procurement AI takes demand forecasting to the next level by analyzing past procurement data and using predictive analytics to make highly accurate forecasts for future needs. Modern technology solutions utilize AI to examine historical trends, seasonal patterns, and consumption behaviors, offering predictions that far surpass traditional methods.
What sets AI-powered analytics apart from traditional analysis is the ability to factor in multiple external influences, like market shifts, supply chain disruptions, or geopolitical risks. For example, if procurement AI notices a sudden increase in raw material prices or identifies potential disruptions due to geopolitical tensions, it can alert the procurement team immediately. With this advance warning, procurement professionals can adjust their procurement strategies in time and prevent potential financial losses.
Purchase order creation
Generative AI in procurement streamlines the process of creating purchase orders (POs) from approved purchase requisitions. Once the requisition is approved, instead of manually inputting information into the order, purchasing agents can just witness the AI system automatically transfer key details like item descriptions, quantities, supplier names, and pricing from the PR to the PO. Such automation reduces the risk of human error, cuts down on administrative work, and accelerates the entire procurement cycle.
OCR for invoice scanning
AI-enhanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems improve invoice processing by accurately reading and extracting important details like vendor names, item descriptions, PO numbers, prices, and payment terms from images or PDF files. Extracted data is then automatically added to the digital invoices in the procurement system, saving your team from the hassle of manual data entry.
Precoro, for instance, leverages AI-enhanced OCR capabilities to handle various document formats, including PDFs, scanned images, and emails, all in multiple languages. This is an AI in procurement example of how to eliminate manual data entry, significantly reducing the risk of errors and saving valuable time. By automating the extraction process with AI, procurement teams can focus on more strategic tasks while AI continuously improves in accuracy and efficiency.

Chatbots and digital assistants
AI-powered chatbots and digital assistants are other AI in procurement examples of changing how procurement teams access information and manage tasks. In procurement, AI-powered digital assistants can instantly answer queries about supplier details, contract terms, order statuses, or spend analytics without the need for employees to browse the data. For instance, a procurement manager can ask a chatbot, “What’s the status of our shipment with Supplier X?” and get an accurate response in seconds.
Advanced chatbots can also proactively send alerts with important updates, such as contract renewal dates or potential supply chain disruptions. Acting as 24/7 assistants, AI-powered chatbots don’t need days off and help teams stay ahead of potential issues and improve overall efficiency.

Types of procurement AI
At its core, the term “AI” refers to any algorithm or system that exhibits behavior considered “intelligent.” AI for procurement, therefore, encompasses various technologies and techniques that can perform certain sourcing, purchasing, and operational tasks that would normally require human intelligence.
In general, AI is categorized into weak AI (or narrow AI) and strong AI (or general AI). Weak AI is designed to perform specific tasks, like automating processes or analyzing data. Strong AI, on the other hand, is capable of performing a wide range of tasks across various domains, mimicking human reasoning and decision-making.
AI used in procurement today falls under weak AI. These technologies enhance efficiency and provide valuable insights, but they can’t adapt to every market challenge or make strategic decisions across the entire procurement process. Below, we break down the key types of AI in procurement and show what each one brings to the table.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that focuses on algorithms that enable systems to learn from data and improve over time without explicit reprogramming. In procurement, ML is widely used for tasks in predictive analytics and optimization of various operational tasks.
For example, ML algorithms analyze historical procurement data to uncover emerging trends and forecast future demand, supplier performance, and price fluctuations. As these algorithms process more data, they “learn” from new inputs and refine their predictions to provide increasingly accurate outcomes.
AI in procurement use cases:
- Identifying spending patterns and uncovering cost-saving opportunities.
- Predicting potential supply chain disruptions or supplier performance issues.
- Anticipating future procurement needs based on historical data and emerging trends.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing (NLP) enables machines to understand, transform, and generate human-like language. It’s especially useful in procurement when dealing with emails, contracts, and other forms of supplier communication.
NLP allows procurement systems to analyze and extract meaningful insights from the textual sources. For example, NLP can automate contract reviews, identifying key clauses, deadlines, and potential risks within legal documents. AI detectors can also help ensure that automatically generated procurement reports or supplier communications maintain authenticity and transparency by distinguishing between human-written and AI-generated text.
AI in procurement use cases:
- Automating contract analysis, flagging compliance issues, and managing renewals.
- Streamlining supplier communications by automating responses to inquiries and processing quotes.
- Extracting key data from invoices (for example, PO numbers and line items) to automate matching and approval.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses advanced neural networks to analyze data in ways that mimic human cognition. Unlike traditional machine learning models, deep learning can handle unstructured data (like text, images, or audio) and learn complex patterns within large-scale data sets without explicit programming for every task.
In procurement, deep learning is valuable for tasks like demand forecasting, market analysis, and fraud detection, where large volumes of diverse and unstructured data need to be processed. By recognizing intricate patterns and correlations, deep learning models can deliver more accurate predictions and uncover insights that traditional methods might overlook.
AI in procurement use cases:
- Analyzing data from multiple sources to predict demand trends with greater accuracy.
- Detecting unusual or fraudulent behavior patterns in supplier transactions.
- Leveraging data patterns to recommend actions like supplier negotiations or risk mitigation strategies.
Generative AI in procurement
Gen AI in procurement refers to a type of AI that not only analyzes existing data but also creates new, valuable outputs based on that data. Unlike traditional AI, which is designed to recognize patterns and make predictions, generative AI in procurement can generate unique outputs, such as text, images, or even sourcing or purchasing strategies.
To function, generative AI models are typically trained on large datasets, which can include historical purchasing data, supplier performance data, market trends, and more. Gen AI in procurement learns from discovered patterns within the datasets, developing the ability to produce unique content or solutions that align with those learned patterns.
Generative AI in procurement use cases:
- Automatically generating purchase orders from requisitions or contracts based on supplier information.
- Creating reports or insights from procurement data for better decision-making.
- Automating supplier communications, for instance drafting responses to inquiries or generating quotes.
- Assisting in demand forecasting by generating predictions based on historical data.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) refers to software robots, or “bots,” that automate repetitive, rule-based tasks. While RPA isn’t traditional AI (it doesn’t involve learning from data or decision-making), it plays a crucial role in AI-driven procurement by streamlining mundane tasks and allowing humans to focus on more strategic activities.
In procurement, RPA is commonly used to automate routine processes like data entry, order processing, and invoice matching. By eliminating manual steps from procurement procedures, RPA helps reduce errors, speed up workflows, and cut costs.
AI in procurement use cases:
- Automatically matching invoices to purchase orders and goods receipts.
- Generating purchase orders based on demand forecasts or inventory levels.
- Automating the collection and entry of supplier information from emails into procurement systems.
Cognitive Procurement (AI-Driven Procurement)
Cognitive procurement is an advanced AI in procurement, an example of how AI capabilities extend beyond basic automation. By adopting cognitive procurement principles, companies enable implemented systems to learn and make decisions similar to human thought processes. These systems integrate multiple AI technologies — such as ML, NLP, and RPA — into a cohesive, intelligent platform that continuously adapts to the unique demands of a given procurement team and improves its decision-making capabilities.
Unlike traditional procurement tools, cognitive procurement platforms can automate entire workflows, predict market trends, and provide deep, data-driven insights into procurement activities. These AI procurement systems are designed to learn from historical data and external inputs, making them highly flexible and scalable as they evolve with the changing needs of the organization.
AI in procurement use cases:
- Managing the entire procurement process, from supplier identification and onboarding to purchase order management and invoice processing.
- Recommending the best suppliers based on performance, cost, risk, and other factors, improving supplier selection and negotiations.
- Predicting market conditions and suggesting adjustments to the company's procurement strategies, ensuring businesses remain competitive and cost-efficient.
Interestingly, while cognitive procurement systems can automate a lot of tasks, they still require human oversight and guidance. These AI procurement tools operate within predefined parameters and decision-making frameworks based on the data they analyze. They don’t have the capability to independently reason, or adapt to new tasks without human intervention, which means cognitive procurement is also a weak AI.
Currently, strong AI isn’t yet used in procurement because it’s still in the realm of research and development. The procurement AI tools available today are designed to address specific challenges, focusing on optimizing tasks that are repetitive, data-driven, and rule-based. In the end, human expertise is still essential for the more complex and strategic decisions that require profound judgment.
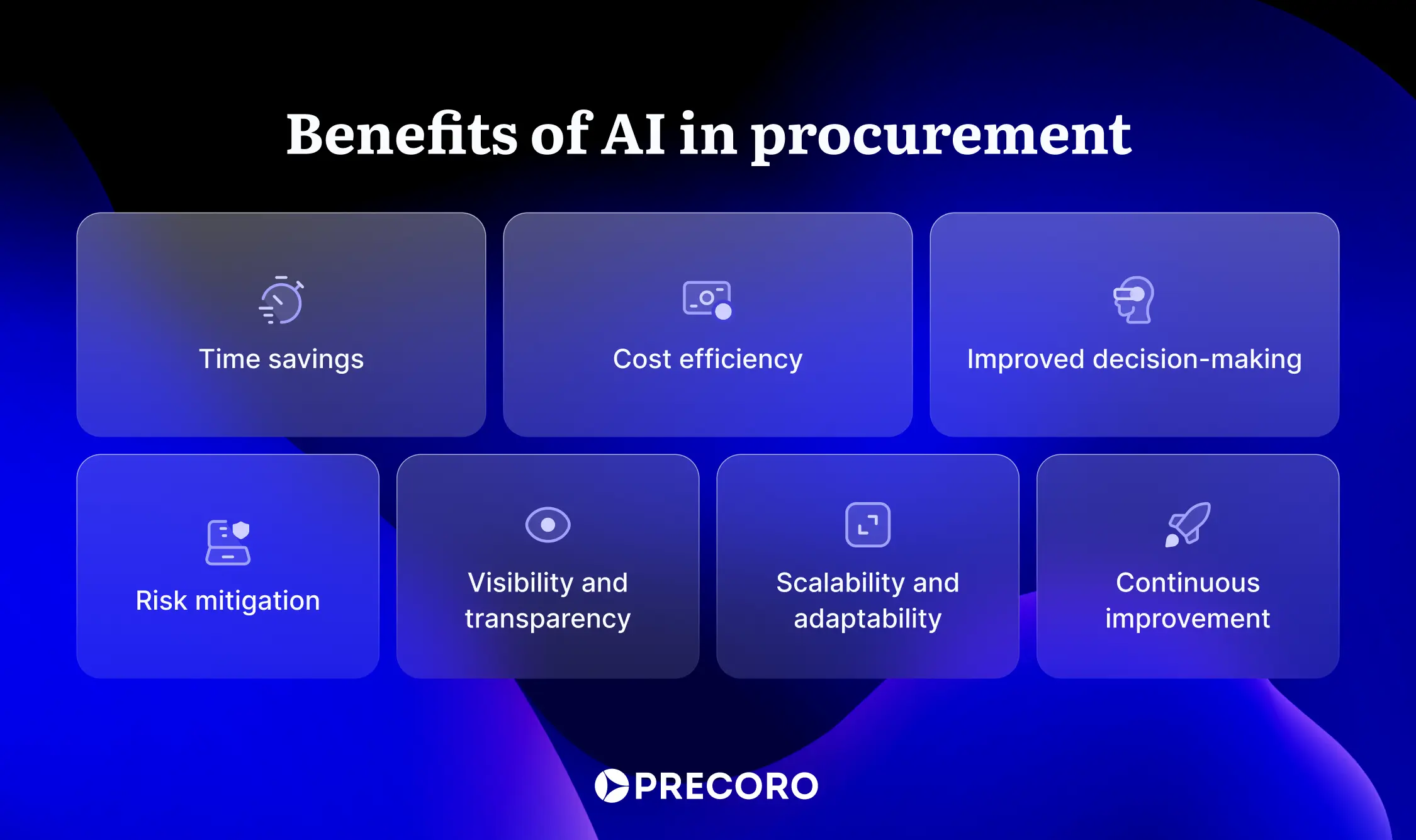
Benefits of AI in Procurement
From saving time to making smarter decisions, here are the key benefits of AI and procurement teams working together:
Time savings for your team
The use of AI in procurement brings a whole new level of efficiency by slashing the time spent on repetitive, manual tasks like data entry, vendor comparisons, and invoice matching. What might take a human hours (or even days) can be completed by AI in a matter of minutes.
Moreover, generative AI in procurement not only speeds up tasks but also creates tailored workflow solutions, customized reports, and more. It’s not just about speed but also about making the procurement team’s life easier. By cutting out bottlenecks, AI for procurement ensures faster approvals, quicker payments, and smoother workflows. That means your team can ditch the busywork and dive into what really matters: building stronger supplier relationships, nailing better deals, and uncovering cost-saving opportunities.
Cost efficiency
AI for procurement helps teams reduce operational costs by automating repetitive tasks like data entry, invoice processing, and spend analysis. This automation not only cuts down on manual labor but also minimizes human error, leading to fewer costly mistakes.
AI also helps ensure informed financial decisions by analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying cost-saving opportunities. For example, AI for procurement can detect maverick spending, optimize supplier selection, and highlight areas for better negotiation based on historical performance data. These insights allow procurement teams to make more cost-effective choices that reduce expenses across the board.
According to Deloitte, among companies that have piloted or deployed AI in procurement, around 50% have reported a doubling of return on investment (ROI) compared to traditional methods. With some advanced implementations, businesses have seen their ROI exceed five times the original investment, underscoring the powerful cost-saving potential of AI use cases in procurement.
Improved decision-making
AI transforms procurement decision-making from guesswork to precision. Instead of sifting through endless spreadsheets or relying on gut feeling, teams can use procurement AI to quickly analyze vast amounts of data for valuable insights — patterns, trends, and opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed. This mirrors how AI marketing tools analyze consumer behavior, predicting trends and optimizing campaigns based on real-time data.
Take supplier selection, for example. AI doesn’t just look at the prices of goods — it can examine historical supplier performance, delivery reliability, and even factors like customer service. This allows procurement AI to recommend the most reliable suppliers, offering the procurement team a solid, data-backed foundation for making a decision. Then, generative AI in procurement can draft contracts based on real-time data.
But it doesn’t stop there. AI for procurement can also help teams anticipate future purchasing needs by forecasting market demand based on past trends, helping companies stay ahead of potential supply shortages or overstocking. However, it’s important to remember that predictions of procurement AI aren’t perfect and can be impacted by unexpected supply chain disruptions or anomalies in the market.
Risk mitigation
AI is like a radar system for potential risks in procurement, constantly scanning both historical data and real-time external factors to detect early warning signs before problems snowball. For instance, if a supplier shows signs of financial instability or drops in performance metrics, AI for procurement can flag these issues early, allowing procurement teams to take proactive steps to find alternative suppliers before any disruptions occur.
Additionally, AI can help companies track compliance with supplier contracts, ensuring that terms like pricing, delivery schedules, and product quality are being met. This way, procurement teams can avoid overspending due to contract violations or overlooked terms.
Moreover, AI in procurement enhances a company’s risk mitigation capabilities that extend beyond individual suppliers. Artificial intelligence can analyze broader patterns in supply chain data, stemming both from internal sources like inventory levels and external factors such as weather events, political instability, or market volatility. This allows companies to stay ahead of potential supply chain disruptions, minimize costly delays, and keep operations running smoothly.
Visibility and transparency
AI for procurement offers a practical, real-time window into spending, giving teams a crystal-clear picture of where their money is going. By analyzing supplier invoices, purchase orders, and contracts, AI can quickly flag areas where expenses may be higher than expected, identify opportunities for consolidating purchases, or even spot missed discounts. This helps procurement teams act fast to optimize their spending and improve cost efficiency.
Additionally, AI bridges the gap between procurement and finance. By providing a unified view of procurement data, AI for procurement helps ensure that both teams are aligned on budgeting and spending forecasts. It also simplifies budgeting processes and helps predict future costs based on past spending patterns, making it easier to stay within budget and achieve financial goals.
Scalability and adaptability
As businesses grow, their procurement needs naturally become more complex. AI in sourcing and procurement supports this growth by automating repetitive tasks and allowing procurement teams to manage an increased volume of purchases without sacrificing efficiency.
Whether your business is expanding into new markets, onboarding more suppliers, or adjusting to shifting demand, AI can handle the heavy lifting. Machine learning can automate supplier assessments, while generative AI in procurement can streamline purchase order creation, adapting to new challenges and opportunities as they arise.
Continuous improvement
Procurement AI systems aren’t static — they get smarter over time. As AI tools process more data and receive feedback, they continuously refine their algorithms, becoming more accurate and efficient. This means AI for procurement can identify high-performing suppliers with increasing success, predict demand with greater precision, and uncover inefficiencies in processes that might have gone unnoticed earlier.
Take supplier selection, for example. Early in its use, AI might highlight suppliers considering just basic criteria like cost and delivery times. However, as the system learns more about each supplier’s performance, it can factor in nuances like quality consistency or customer service reliability, providing even more precise recommendations.
Similarly, generative AI in procurement improves over time by learning from past data. Initially, it may draft basic documents like purchase orders or supplier contracts using standard templates.
As gen AI in procurement processes more data, it becomes capable of generating more complex, customized documents, such as contract clauses that reflect updated pricing models, supplier performance, or changing procurement conditions. To better leverage these capabilities, some teams are turning to ChatGPT courses to upskill procurement professionals in prompt engineering and AI-assisted document generation.
Challenges of AI in procurement
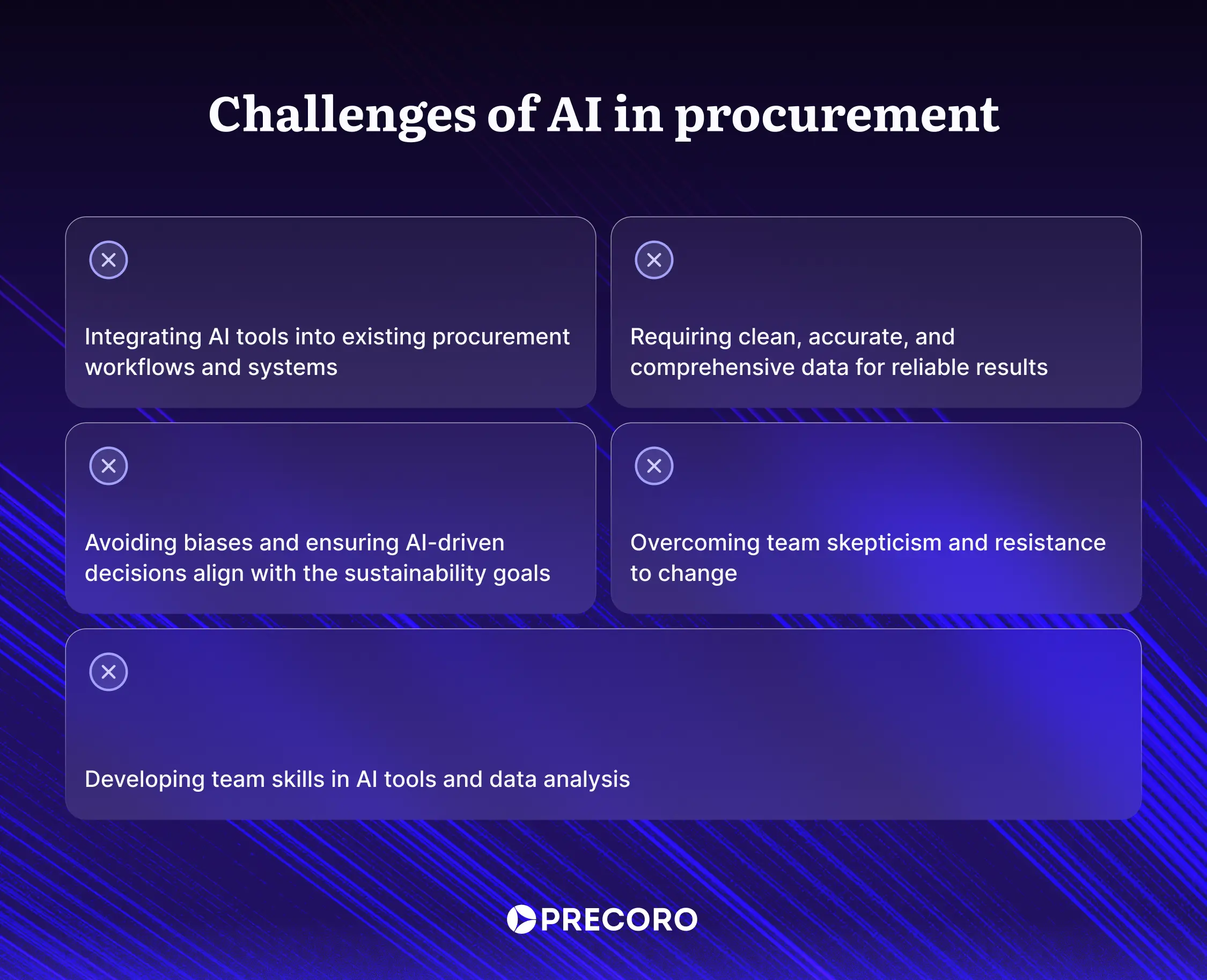
AI offers significant potential to improve procurement, but its adoption comes with challenges and risks that organizations must navigate carefully.
Adoption and integration
One of the biggest challenges businesses face when implementing AI for procurement is integrating it with their existing systems. Many procurement operations still rely on legacy ERP platforms that were never built to support modern AI tools. These older systems often operate in silos, with limited flexibility, which makes it difficult to align AI solutions without disrupting established processes.
Additionally, procurement processes themselves can add another layer of complexity. The need for simultaneous management of multiple suppliers, contracts, and compliance requirements leads to vast amounts of data that often exist in scattered or inconsistent formats. Procurement AI tools struggle to deliver value when they aren’t provided with clean, structured, and coherent data.
The combination of outdated systems and fragmented workflows creates a significant barrier for businesses looking to smoothly implement AI.
Data dependency
AI for procurement is only as good as the data it can access. Think of it as looking for directions with a map full of missing roads and mislabeled cities. If the data is incomplete, inconsistent, or riddled with errors, the AI’s outputs will be unreliable. For example, flawed historical data about purchases might lead AI to paint an inaccurate expense picture and completely miss key spending trends.
The challenge gets even bigger when procurement data comes in a chaotic mix of formats. Invoices, supplier contracts, and emails often exist in unstructured forms, with inconsistent details and messy inputs. Generative AI in procurement is built to handle distorted data, but when the noise gets too loud — think scattered formats, duplicate entries, and gaps — AI struggles to provide valuable insights. This makes it hard for organizations to trust AI-generated recommendations and predictions, limiting its real value in procurement.
Ethical concerns
Generative AI in procurement, while powerful, introduces ethical concerns that need careful consideration. Like other AI systems, it carries the risk of perpetuating or amplifying biases, especially in areas like supplier selection. If generative AI in procurement is trained on historical data that includes biased decision-making — such as favoritism toward larger suppliers or certain geographic regions — it may unintentionally prioritize those same suppliers. This could result, for example, in overlooking smaller, minority-owned businesses or suppliers with better higher prices but ethical practices.
Moreover, generative AI could create procurement models or contracts that are heavily influenced by profit-driven factors without accounting for ethical considerations like sustainability and social responsibility. Without proper management, gen AI in procurement might design strategies that prioritize efficiency and cost savings over the broader values a company upholds, such as supporting diverse suppliers or addressing environmental impact. Therefore, businesses need to implement measures to ensure generative AI not only supports financial business goals but also aligns with ethical and social standards of the company.
Resistance to change
Procurement teams often resist the adoption of artificial intelligence because they see it as a threat to their job security and undermining their expertise. These professionals have honed skills over the years, managing supplier relationships and navigating the complexities of negotiations, risk management, and procurement compliance. The idea that a machine could handle some of their tasks makes them think that the use of AI in procurement undermines the value they’re bringing to the table through human experience and judgment.
Furthermore, procurement professionals often question whether AI can truly grasp the human elements of procurement, such as supplier reliability during crises or navigating cultural differences. These nuanced factors are tough for algorithms to capture, creating a gap between AI’s potential and the real-world, relationship-driven nature of procurement.
Skills and expertise
The use of AI in procurement isn’t just about having the latest tech — it’s about ensuring your team has the right skill set to make the most of it. Investing in procurement AI tools without the expertise to operate them effectively can be like buying a high-end sports car but never learning how to drive.
This challenge is even more urgent because the use of AI in procurement isn’t a “set it and forget it” solution. Unlike simpler automation tools, AI requires ongoing attention and training. Your team needs to understand not just how to operate the software, but how to interpret the data it generates, adjust algorithms as needed, and use correct AI-driven insights to make more informed decisions.
Mitigation strategies: How to address procurement AI risks and challenges
Successfully integrating AI in sourcing and procurement is like navigating a tricky but exciting journey. Here are some strategies to help you overcome the above-mentioned risks, make the most of AI’s potential, and keep things human-centered while exploring AI in procurement examples.
For smooth adoption and integration
To ensure a smooth implementation of AI in sourcing and procurement, start by assessing your current procurement infrastructure — ERP systems, databases, and workflows — to spot gaps that could hold back AI adoption. Look for limitations around data accessibility, integration, and automation.
If legacy systems are too outdated or inflexible, consider moving to modern, cloud-based platforms. These offer better scalability, integration capabilities, and compatibility with today’s AI tools, many of which are built to work seamlessly with leading ERPs and procurement software.
Instead of overhauling everything at once, take a modular approach. Start with procurement AI tools that solve specific problems, like invoice matching, supplier performance analysis, or spend forecasting. By introducing AI in smaller steps, you can test its value in real workflows and achieve quick wins while avoiding disrupting day-to-day operations. This phased approach also helps teams adapt gradually and refine processes as they go.
Finally, create a clear integration plan and involve key stakeholders (like IT, procurement, and finance) from the start. By aligning goals, timelines, and technical requirements across all involved departments, you can ensure a smoother rollout and set the stage for maximizing AI’s impact on procurement.
For data cleanliness
Evaluate your current procurement data. Look for inconsistencies, gaps, and duplicates, and pinpoint key sources of unstructured data — such as invoices, supplier contracts, and emails. This audit will highlight problematic areas and give you a clear starting point for further improvements.
Next, focus on data cleansing: remove duplicates, fix errors, and fill in missing information. Standardize data formats to ensure that supplier names, price currencies, and order or delivery dates follow consistent patterns. If this process feels overwhelming, consider using automated data-cleaning tools to streamline the work.
It’s also a good idea to implement a procurement platform with AI-enhanced Optical Character Recognition (OCR) like Precoro to convert unstructured data from invoices and other documents into standardized formats. This improves the accuracy and quality of data fed into AI systems, enhancing the model’s successful training and excellent performance.
Remember, ensuring high data quality is a marathon, not a sprint. Set up smart data governance practices to keep your procurement data fresh, accurate, and consistent. Simple measures, like automated inspections to validate invoices or supplier details, can prevent mistakes from happening before they mess things up, keeping your AI working at its best.
For the sustainability cause
To tackle bias in AI-driven procurement, companies need to train their AI systems on a diverse mix of data. This means considering all kinds of suppliers — large, small, local, minority-owned — instead of sticking to the usual options. When setting up your models, remember to factor in important ethical criteria like sustainability and social responsibility.
Regular “bias checks” are also a must. Think of it like a routine “health check-up” for your AI. By reviewing how the system is performing and making sure it’s not favoring certain suppliers or overlooking others, you can catch any biases early on. This might mean tweaking the data or algorithms to keep things balanced. Explainable AI (XAI) can help here by making the decision-making process transparent so your team can understand why certain choices are made and spot any hidden biases.
Finally, remember that even generative AI in procurement should be a trusty sidekick, not the boss. Procurement teams need to stay involved in the company’s agenda and bring the human touch to decisions. Sometimes it’s necessary to go beyond the bare data and consider factors like ethics and social impact. By blending AI’s smart insights with human judgment, businesses can make procurement decisions that are not only financially beneficial but also responsible.
For embracing AI
To address resistance to procurement AI adoption, businesses should focus on creating a clear understanding of AI’s role as an enabler, not a replacement. Generative AI in procurement is designed to take over time-consuming and data-heavy tasks, freeing procurement professionals to focus on higher-value activities.
A key step is involving procurement teams early in the AI integration process. Showcasing early success stories (for example, faster invoice processing, reduced errors, or more efficient spend analysis) can also help build momentum for AI adoption. Demonstrating tangible benefits from the outset encourages teams to embrace the technology and see it as a valuable asset.
To ensure the right skill set
To make sure your team has the right skills to handle AI for procurement, start with figuring out what these skills are. Generative AI in procurement takes things up a notch compared to traditional AI, so your team will require more specialized expertise. They’ll have to understand data science and machine learning, especially for fine-tuning AI systems.
Strong skills in data analysis are also a must to make sense of the AI’s output and ensure it aligns with procurement goals. Plus, a solid understanding of procurement processes is key to help AI generate useful company-tailored solutions, like picking the right suppliers or drafting contracts.
It’s a good idea to provide the procurement team with training programs or workshops focused on AI fundamentals, as well as offer them hands-on experience with the tools they will be using to integrate AI and procurement. This can help employees feel more confident in using AI effectively and encourage a culture of continuous learning. As AI technology evolves rapidly, staying updated on the latest trends and tools is essential.
In addition, consider bringing in AI experts or consultants to guide the initial stages of AI adoption and help bridge any knowledge gaps. You can also create cross-functional teams with both procurement experts and data scientists to ensure a blend of domain knowledge and technical expertise.
Alternatively, if training your team on complex procurement AI tools feels daunting, you can opt for systems that implement AI in areas where it provides significant value without requiring special skills. Precoro, for example, offers AI-powered OCR for invoice scanning and digitization. All you need to do is upload the invoice or set it to be automatically redirected to the AP inbox, and Precoro will handle the rest — making AI accessible and efficient without the need for deep technical expertise.

The future of AI and procurement
As AI continues to streamline procurement, the future promises even more transformative changes. From autonomous procurement systems to innovative sustainability tracking, AI’s potential is expanding rapidly. Here’s a glimpse into what the future holds for AI in procurement.
Autonomous procurement evolution
n the future, AI will take procurement to new heights, stepping in to handle most of the data-intensive tasks that once drained valuable human time and resources. Total process automation will mean no human involvement is required for routine tasks like approvals, compliance, and reporting. Machines will be capable of independently identifying and acting on opportunities for savings and value creation. Imagine AI autonomously selecting suppliers based on real-time performance data and managing orders with minimal to none input by employees.
Generative AI in procurement is important to mention here as it could move beyond basic document creation to crafting complex, data-driven supplier engagement strategies. For example, generative AI might analyze supplier performance, market conditions, and organizational goals to recommend not just which suppliers to engage but how to structure partnerships for maximum value.
AI-driven contract negotiation
Picture a future where contract negotiations happen at the speed of AI. Well, soon enough, it can be a reality. According to Gartner, by 2027, 50% of organizations will use AI-powered tools to help with supplier contract negotiations, including analyzing risks and editing contracts..
Instead of weeks of back-and-forth, generative AI in procurement could autonomously analyze market conditions, supplier data, and legal frameworks, and then generate contract terms that are not only favorable but also tailored to real-time market conditions. By sifting through mountains of data, AI will pinpoint the best possible deals, flagging opportunities for better pricing, favorable terms, or advantageous delivery conditions that might otherwise be missed.
Balancing cost and sustainability
In an increasingly complex business world, balancing cost-efficiency strategies with sustainability goals is one of the greatest challenges procurement teams may ever face. However, with AI, this delicate balance becomes achievable. Imagine AI identifying suppliers who offer the best combination of cost and sustainability — where carbon footprints, resource usage, and ethical sourcing practices are factored into every decision, alongside pricing and performance.
This evolution in procurement will allow companies to make smarter, more responsible decisions that align with both their financial objectives and sustainability commitments. As artificial procurement intelligence continues to evolve, it will also provide real-time insights to help businesses track their environmental impact, ensuring that procurement decisions align with both profit goals and environmental responsibility.
The future of AI in procurement will mean more than just cost-cutting; it will create a path for companies to lead with integrity, driving profitability while reducing their environmental footprint.
Redefining procurement roles
The shift to more autonomous AI procurement systems will redefine the role of procurement professionals in general, turning them into strategists and relationship managers, rather than task performers. Instead of being bogged down by repetitive processes, they will focus on crafting long-term strategies, navigating complex market dynamics, and ensuring procurement aligns with broader business goals. The synergy between AI-driven automation and human expertise will create a procurement function that is faster, smarter, and more value-oriented than ever before.
Frequently Asked Questions
AI streamlines procurement by automating data-driven tasks like spend analysis, supplier evaluation, and purchase order creation. It enhances demand forecasting, optimizes contract management, and uses OCR for accurate invoice processing. AI-powered chatbots provide real-time updates, boosting purchasing efficiency. In general, by handling routine tasks, AI frees procurement teams to focus on strategic goals, improving the company’s overall performance and reducing costs.
AI and procurement will evolve together to transform the sourcing, purchasing, and supplier management processes. Thus, AI will not replace procurement as a function but will work alongside procurement professionals and simplify rule-based, data-laden, and repetitive tasks for them.
Generative AI in procurement is a type of AI that can create content and solutions based on the data it’s trained on. For example, it can draft supplier contracts, suggest alternatives to meet sustainability goals, or simulate purchasing scenarios. Instead of just analyzing data, gen AI in procurement produces helpful outputs, making it faster and easier for procurement teams to complete their tasks while improving decision-making.
Companies use machine learning in procurement to analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns. AI is used, for example, for predicting demand, evaluating supplier performance, detecting fraud, and automating tasks like invoice processing. Machine learning helps procurement teams save time, reduce costs, and improve accuracy.
Procurement AI in a nutshell
In conclusion, the use of AI in procurement is reshaping the landscape by automating time-consuming, data-heavy tasks and giving involved teams the opportunity to focus on more strategic work. There are many AI use cases in procurement — from streamlining supplier evaluations to improving demand forecasting and simplifying invoice processing.
Some challenges for implementing AI still exist. For instance, skepticism around generative AI in procurement managing the human side of operations or the need for smooth data integration still. Yet, they’re far from impossible to overcome. With clear communication, high-quality training, and gradual implementation of AI-powered tools, these obstacles can be tackled head-on and turned into opportunities for growth and innovation.
As artificial intelligence technology keeps evolving, its ability to cut costs, boost data accuracy, and uncover spending or supplier insights will only grow. However, the future of AI and procurement isn’t just about the latest tech — it’s about using AI to compliment human expertise for making more informed decisions, strengthening supplier relationships, and ensuring long-term, sustainable growth.