14 min read
Sustainable Procurement: Everything You Need to Know
Discover how sustainable procurement is revolutionizing business practices and driving a positive impact on our planet and society.
March 21 was the second annual iteration of World Sustainable Procurement Day, an online event organized by the Sustainable Procurement Pledge team, SPP Chapters, SPP Champions, and partners to raise awareness about the importance of ethical procurement and to share the best sustainability practices with organizations worldwide. In light of this event, we here at Precoro thought it would be a great time to go over the fundamental principles of sustainable procurement.
Nowadays, more and more businesses are recognizing the significance of their environmental impact and the need for strong social responsibility. Thus, prioritizing sustainable procurement has become a critical component of companies' policies; by doing so, organizations promote transparency, fairness, resource efficiency, and ethical practices while enhancing their brand image and competitiveness.
In this article, we will explore the benefits of sustainable procurement and share best practices that procurement leaders can adopt to contribute to a greener, fair future.
Keep reading about:
- Sustainable Procurement, Its Meaning and Importance
- 3 Pillars of Sustainable Procurement Strategy
- Benefits of Sustainable Procurement
- Best Practices of Sustainable Procurement
- Frequently Asked Questions
Sustainable Procurement, Its Meaning and Importance
Sustainable procurement is a process by which companies obtain the needed goods and services while incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. Companies who choose to adopt sustainable procurement practices have their own reasons for doing so, and these reasons can fall into any of the above categories.
The importance placed on sustainable practices might have to do with company stakeholders' desires to leave a more responsible footprint on the planet, or they might feel external pressure from competition and consumers to do so. Let's delve deeper into what makes sustainable procurement important for companies.
Attention to climate change
Climate change is not just looming over the horizon; it already affects all spheres of our lives. Examples of its adverse effects include increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, rising sea levels, loss of biodiversity, damage to infrastructure and homes, food insecurity, water shortages, and increased rates of respiratory illness and heat-related illnesses.
Companies contribute to a significant portion of greenhouse gas emissions, resource depletion, and ecological disruption. Thus, it's the responsibility of every business to pursue policies that reduce their environmental impact and help build a more sustainable future.
Optimizing the supply chain can play a significant role in reducing a company's adverse influence on the environment as their Scope 3 emissions are directly affected by their suppliers. Did you know that a supply chain of a typical consumer's company is responsible for more than 80 percent of its greenhouse gas emissions and more than 90 percent of the impact on air, land, water, biodiversity, and geological resources? These figures illustrate how important it is to make sure that your suppliers share your values and adopt sustainable practices.
Meanwhile, according to the International Labour Organization (ILO), climate change significantly impacts jobs: by 2030, 2.2 percent of total working hours worldwide (equivalent to 80 million full-time jobs) will be lost due to high temperatures.
In our world, everything is interconnected, and each small step counts, especially when we have biodiversity, resources, jobs, and human lives at stake.
Ever-growing social awareness about human rights
Consumers are becoming more concerned about the social impact of their purchases and want to know that companies' supply chains are free from human rights abuses and promote fair and ethical practices. As a result, stakeholders such as investors and regulators are increasingly holding companies accountable for the social and ethical implications of their procurement decisions. Here are some examples of how this is driving sustainable procurement:
Human rights due diligence: Many companies are now conducting human rights due diligence in their supply chains to identify and address potential human rights risks such as discrimination (unequal pay or harassment) based on race, gender, religion, or other characteristics, exposing workers to hazardous substances without the protection, violating the land and resource rights of indigenous peoples or local communities, and more.
The measures that should be taken involve assessing current and potential suppliers' human rights records, monitoring their performance, and taking corrective action when necessary. For example, Unilever, a consumer goods company, has a responsible sourcing policy that includes human rights due diligence and requires suppliers to adhere to its human rights principles.
Departure from forced labor: Forced labor is a form of modern-day slavery that is usually realized through debt bondage and human trafficking. Companies are under pressure to take action to prevent and eliminate forced labor in the production of their goods. For example, in 2020, Apple announced it would stop doing business with suppliers using forced labor.
Boycott of child labor: The use of child labor is a major human rights issue in industries such as textiles, agriculture, and mining. Consumers increasingly demand that companies ensure products are not made by children. Many organizations have responded by introducing policies and practices to prevent and address child labor in their supply chains. For example, Nestlé, a renowned food and beverage company, has a Child Labor Monitoring and Remediation System to identify and prevent child labor in its cocoa supply chain by communicating directly with children at risk, their families, or their communities. In 2022, Nestlé also announced an innovative plan to tackle child labor risks and implement other sustainable practices.
Social certification schemes: Social certification schemes are programs that certify that a product or organization meets certain social or ethical standards. They help companies ensure their supply chains are free from human rights abuses and promote fair and ethical practices. For example, the Fairtrade International certification scheme assures companies that the farmers and workers in developing countries who supply their products receive a fair price and operate in decent working conditions.
Legal and regulatory requirements
The importance of adopting sustainability in procurement is also determined by laws and regulations introduced by many countries that require companies to implement sustainable procurement practices. Here are some examples:
Government regulations: Governments worldwide have introduced policies and regulations to promote sustainable practices. For instance, the EU's Public Procurement Directives require that public procurement processes consider environmental, social, and ethical criteria. Other examples include the EU's Circular Economy Action Plan and the US Green New Deal.
International standards: International standards, such as the ISO 14001 and ISO 26000, provide guidelines for companies to establish and maintain sustainable practices. These standards cover a range of issues, including environmental management systems, social responsibility, and sustainable supply chain management.
Industry-specific regulations: Many industries have specific regulations to ensure procurement choices are ethical. For example, in the textile industry, several standards and certifications, such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Better Cotton Initiative (BCI), require companies to use sustainable materials and reduce the environmental impact of their operations.
Reporting requirements: In order to demonstrate their commitment to procurement sustainability and build trust with stakeholders, companies are often required to disclose their sustainability performance. The Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) is a widespread framework that provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for sustainability reporting.
3 Pillars of Sustainable Procurement Strategy
Sustainable procurement practices fall into 3 main categories: social responsibility, environmental protection, and economic prosperity. Let's see what each of them entails.
Social Sustainability
Social sustainability refers to the ethical and social impact of purchasing decisions on the broader community, including employees, suppliers, customers, and other stakeholders. Measures are taken to promote fair labor practices, diversity and inclusion, human rights, and community development.
Examples of social sustainability in procurement include:
- Sourcing from suppliers who provide fair wages and safe working conditions.
- Including women-owned and minority-owned businesses in the supply chain.
- Engaging with local communities to understand their needs and support local development.
Environmental Sustainability
Environmental sustainability measures focus on mitigating the impact of procurement decisions on the natural environment. Such measures aim to reduce carbon emissions, conserve natural resources, minimize waste and pollution, and promote sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
Some examples of environmental sustainability in procurement are:
- Sourcing from suppliers using sustainable materials and production methods.
- Promoting circular economy principles.
- Designing products and packing materials in a way that minimizes waste.
Economic Sustainability
Economic sustainability refers to the impact of procurement decisions on the economic well-being of the organization, its suppliers, and the wider community. For instance, goals in mind might be bolstering the financial value of the company and/or promoting local economic development.
Measures that promote economic prosperity might look like this:
- Using competitive bidding processes to ensure value for money.
- Sourcing from local suppliers to support the local communities and save costs on transportation.
- Investing in renewable energy to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and save money in the long run.

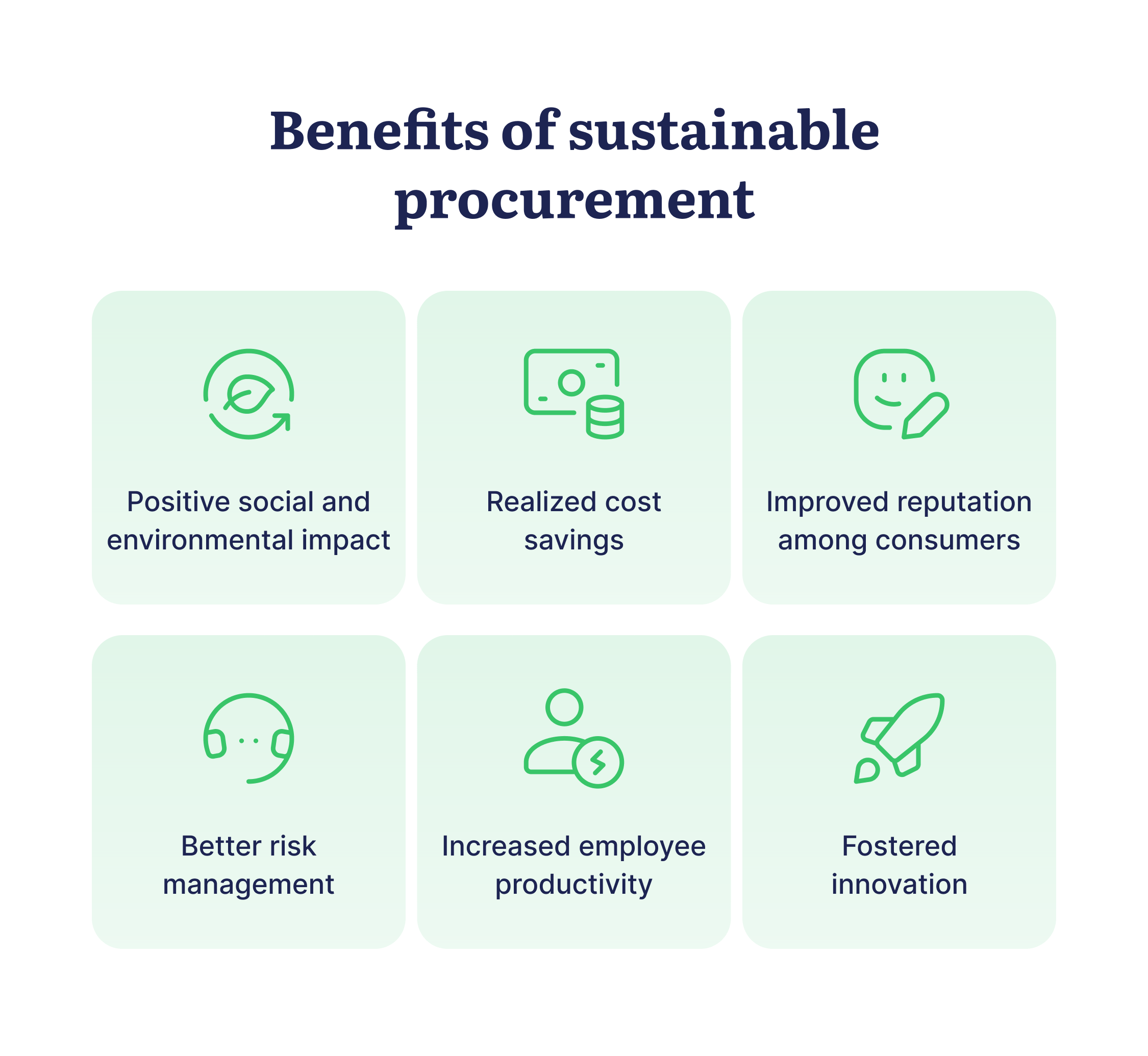
Benefits of Sustainable Procurement
Nowadays, sustainable procurement is not only an ethical obligation but also a strategic choice for organizations to thrive in the long run. Let's consider its key benefits:
Positive social and environmental impact
The first and most obvious benefit is that companies with sustainable procurement practices promote fair labor practices, reduce greenhouse emissions, and minimize waste and pollution. Thus, they contribute to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals, such as reducing poverty, mitigating climate change and environmental degradation, promoting health and well-being, ensuring responsible consumption and production, and much more.
Realized cost savings
While it is true that some sustainable products and methods may have higher upfront costs, sustainable procurement practices can ultimately help companies save money. For example, if a company invests in energy-efficient equipment, such as LED lighting or HVAC systems, it may incur higher upfront costs compared to traditional equipment. However, these energy-efficient products will help the company reduce its energy consumption over time, resulting in lower energy bills. Similarly, if organizations choose products and suppliers that prioritize waste reduction and recycling, they reduce their waste disposal costs.
Improved reputation among consumers
Consumers are increasingly concerned about the environmental and social footprint of the products and services they purchase. By demonstrating a commitment to sustainability, companies gain an advantage over their competitors in the world market. In 2019, 72% of consumers in 11 countries across North America, Europe, and Asia reported buying more environmentally friendly products than they did five years ago, and 81% said they expected to buy even more over the next five years. In 2022 a survey of over 1,000 US adults revealed that 66 percent of consumers and 80 percent of young adults (ages 18-34) are ready to pay more for sustainable products versus less sustainable competitors.
Better risk management
Sustainable suppliers that prioritize ethical and responsible practices reduce the risk of supply chain disruptions. This can ensure supply continuity and security, helping companies to maintain stable operations and meet customer demand. In addition, sustainable procurement practices help companies avoid legal liability by ensuring compliance with regulations and laws related to environmental, social, and labor standards. Thus, organizations avoid costly fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage that can result from non-compliance.
Increased employee productivity
Creating a healthier and more positive work environment can improve employee productivity in the following ways:
- Companies that prioritize sustainability tend to have improved air quality, use healthier and safer materials and equipment, and employees are less likely to be exposed to harmful chemicals. Employees that are physically healthier are more likely to do a better job and stay with the company.
- Procurement leaders can improve employee satisfaction by promoting ethical business practices, for instance, paying fair wages and conducting employee training and development programs to foster career growth. These practices motivate employees to work more diligently, appreciate their workplaces, and build their careers in the company rather than hopping from one organization to another.
- The organization's demonstrated social responsibility and commitment to environmental protection help its workers value and respect it more, encouraging them to stay with the company and contribute to the positive changes it brings to our world.
Fostered innovation
Sustainable policies also have the potential to drive innovation in a company's products and operations in several ways, which include:
- Creation of a new revenue stream through the circular economy model by finding ways to repurpose and reuse waste or byproducts.
- Implementation of sustainable product design using energy-efficient components or manufacturing processes, renewable materials, or those that can be easily recycled or composted.
- Close cooperation with suppliers to develop new sustainable products or processes, which lets a company tap into the expertise of its partners.
Best Practices of Sustainable Procurement
Upholding ecological, economic, and social responsibility takes a holistic and continuous approach. Here are some best practices:
Conduct analysis and reporting
Before implementing new sustainability practices, it's essential to clearly understand the existing procurement process and its ESG (environmental, social, and governance) footprint. Here are some ways in which spend analysis helps companies become more sustainable:
- Reduce waste by identifying duplicate orders and unnecessary spending.
- Identify ways to decrease their environmental footprint by analyzing spend data related to energy usage, transportation, and raw materials and measuring carbon emissions, water usage, and waste generation.
- Determine the company's social impact by tracking employee turnover, supplier diversity, and community investment.
- Reduce the risk of reputational damage by determining whether the company complies with regulations and codes of conduct.
- Evaluate supplier performances regarding on-time delivery and product quality and determine how many suppliers are local.
Spend analysis is crucial for identifying the main risk areas and discovering opportunities to make changes toward sustainable procurement. To simplify this process, businesses can utilize procurement software, like Precoro, which can serve as a centralized database and tracking tool for budgets, suppliers, orders, and delivery. In addition, the tool has a module that analyzes various procurement data and displays it in a visually comfortable report.

Conducting sustainability reporting is crucial for tracking a company's progress. For instance, teams can analyze the life cycle of a product to determine its environmental impact before and after implementing sustainability practices. GRI Standards, which we mentioned previously, provide a widely used framework for sustainability reporting.
Analysis and reporting are nearly impossible without key performance indicators (KPIs), specialized metrics that help determine a company's progress toward its goals. Let's learn more about them.
Use KPIs to track progress
There are many KPIs for sustainable procurement, and deciding which to track depends entirely on the organization and its primary goals. An expansive list of KPIs and their purposes can be found in the study conducted by SINTEF. As procurement experts, here are some KPIs we would recommend starting with:
Percentage of spend on sustainable products/services: This KPI measures the percentage of total procurement spend on products or services that meet the organization's sustainability criteria, such as being environmentally friendly and socially responsible.
Supplier diversity: This KPI measures the diversity of suppliers in the organization's supply chain, including metrics such as the number of women-owned or minority-owned businesses.
Greenhouse gas emissions: This KPI looks at the GHG emissions generated by the organization's procurement activities, including sourcing, transportation, and production.
Waste reduction: This measures the amount of waste generated by the organization's procurement activities, including packaging and product waste, and tracks progress in its reduction.
Ethical sourcing: This KPI helps to assess the organization's compliance with ethical sourcing standards and criteria, such as labor standards, human rights, and anti-corruption policies.
Create a sustainability policy framework
A sustainability policy framework helps companies commit to their goals with concrete actions. Such a document should include the following:
- A clear statement that outlines the organization's commitment to sustainable procurement.
- Concrete goals and targets, such as reducing carbon footprint by 40% by 2030 or increasing the use of renewable energy sources by 20% by 2027.
- Clear roles and responsibilities for all stakeholders involved in the procurement process, including suppliers, business units, and senior management.
- Specific criteria that suppliers must meet to be considered for contracts, such as sustainability certifications and compliance with environmental and social regulations.
- A system for monitoring performance, including regular audits of suppliers and reporting on progress toward achieving sustainability targets.
Assess the sustainability of your suppliers
To determine the sustainability of your supply chain, ask your key suppliers directly about their sustainability goals and metrics or, if they don't have this, send them questionnaires to gather information. You can also request certifications from third-party organizations (ISO, Fairtrade, and more) or their sustainability reports.
Suppose your preferred suppliers don't implement sustainable practices but want to change that; you can move towards that goal together. Your company can even offer training and guidance on sustainable procurement practices if it has more experience in this field.
It's important to mention that sustainability in procurement may also involve sourcing materials and components from local suppliers to reduce transportation distances. However, it's important to evaluate and compare options as specific environmental conditions of some local sites may require the use of more resources, which can have negative impacts on the environment depending on what they are. Additionally, organizations can increase supplier diversity by working with women and minority-owned businesses.
Companies can also incorporate sustainability requirements into supplier contracts, making it a contractual obligation for suppliers to comply with sustainability criteria.
Optimize operations
Let's consider what practices can help companies achieve operational efficiency while being mindful of sustainability:
- Prioritize the use of recycled or renewable materials in products or packaging.
- Implement water conservation measures such as water-efficient equipment, rainwater harvesting, and wastewater recycling.
- Incorporate renewable energy sources, like wind turbines or solar panels, into operations. Of course, not each company can afford to implement such drastic changes. In that case, an organization can prioritize suppliers who already did and, thus, decrease its indirect emissions.
- Optimize transportation of your goods by using electric or hybrid vehicles or partnering with delivery companies that implement green technologies.
- Promote public transport carpooling for business travel to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
In addition, it is important to acknowledge that sustainability encompasses more than just products and their production. It also includes ensuring safe working conditions, fair wages, and protection of worker rights.

Frequently Asked Questions
What are examples of sustainable procurement?
Purchasing products made from recycled materials, sourcing products locally, using eco-friendly packaging, implementing policies that support equal opportunities and combating discrimination, ensuring safe working conditions, and working with suppliers that incorporate fair labor practices are all examples of sustainable procurement.
What are the three pillars of sustainable procurement?
- Environmental sustainability refers to the responsible use of natural resources and the minimization of environmental damage. It involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, conserving resources, minimizing waste, and using renewable or recyclable materials.
- Social responsibility refers to the ethical and moral obligations of an organization to act in ways that benefit society and promote the well-being of its employees. It involves ensuring safe working conditions, preventing discrimination, providing fair wages and benefits, and supporting local communities.
- Economic sustainability refers to the ability of a business to maintain long-term viability and profitability while also balancing economic growth with social and environmental considerations. It involves pursuing financial stability, efficient use of resources, and responsible investment.
What are the objectives of sustainable procurement?
Sustainable procurement objectives include:
- Reducing greenhouse emissions.
- Preserving biodiversity and resources.
- Abolishing child labor and forced labor.
- Reducing inequalities.
- Supporting local and regional economic development and more.
What is a sustainable procurement policy?
A sustainable procurement policy is a document that outlines an organization's commitment to incorporating sustainability principles into its procurement processes. It typically includes concrete goals, roles and responsibilities of stakeholders in achieving sustainability, criteria for assessing suppliers, and performance metrics to measure progress.
In a Nutshell
Sustainable procurement is a strategic purchasing process that goes beyond economic factors. It considers environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles to ensure that organizations acquire products in a way that minimizes negative environmental impacts, promotes positive social outcomes and complies with regulations.
Procurement sustainability has several benefits, including better outcomes for the environment, protection of human rights, cost savings through resource conservation, enhanced reputation and brand value, increased supply chain resilience and efficiency, compliance with regulatory requirements, increased employee productivity, and innovation. It also contributes to achieving the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Sustainable procurement involves a holistic approach to promote ecological responsibility, economic viability, and social equity. Organizations can start small and focus on one or two aspects of sustainability which would still make a great difference. Toward this goal, companies can adopt the following best practices:
- Using specialized KPIs to evaluate the initial business processes with spend analysis and create sustainability reports to track progress.
- Creating a sustainability policy that outlines clear goals, roles, responsibilities, and supplier criteria.
- Assessing suppliers' sustainability practices, requesting certifications, and incorporating sustainability requirements into contracts to ensure sustainable practices throughout the supply chain.
- Optimizing operations when it comes to recycled or renewable materials, water conservation, renewable energy, and transportation to reduce the environmental impact.
- Providing fair wages, safe working conditions, and protection of worker rights to ensure social justice and ethical business conduction.
By implementing these practices, companies can achieve their sustainability goals and contribute to creating a better world for future generations.