33 min read
AI Invoice Processing & Automation Explained
Learn how AI invoice processing automates data extraction, validation, and approvals to reduce processing time from weeks to days.
Invoice processing is still one of the most manual, time-consuming areas of accounts payable. Teams spend days chasing invoices, re-entering data, fixing errors, and waiting for approvals.
Machine learning changes how this work gets done. Instead of relying on rigid rules or manual checks, ML-based invoice processing systems learn from invoice data to extract information accurately and validate it automatically.
This guide explains how machine learning invoice processing works, which features matter in real-world use, and how to implement it effectively.
Read on to find out:
What is AI for invoice processing, and why does your business need it?
How does AI-based invoice processing actually work?
What are the key benefits of AI invoice processing?
What features should you look for in AI invoice processing software?
How can AI handle different types of invoices and exceptions?
Manual vs. AI‑led invoice processing (comparison)
What are the implementation steps for AI invoice automation?
What challenges might you face in machine learning-based AI processing?
Which industries benefit most from AI invoice processing?
Evaluating & selecting AI invoice processing software
What does the future hold for AI invoice processing?
Best practices for AI invoice processing
Frequently asked questions
What is AI for invoice processing, and why does your business need it?
AI invoice processing is transforming the way organizations handle invoice payments by automating data capture, validation, and approval workflows. This technology aims to address many critical inefficiencies of the traditional invoice management pipeline to provide noticeable improvements in terms of speed, accuracy, and cost reduction.
Businesses in many industries are rapidly adopting different AI-powered invoice solutions to get rid of manual data entry, reduce processing errors, and create real-time visibility into their financial operations.
What exactly is AI-powered invoice processing?
AI-powered invoice processing uses artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI and ML) in order to automate invoice data capture, extraction, and validation. Such a system replaces manual data entry. It recognizes invoice formats, extracts the required data, and routes invoices through the correct approval workflows automatically.
This technology is a combination of optical character recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning capabilities that help it process invoices from different sources (emails, PDFs, scanned documents).
The AI-powered invoice processing system has the capacity to learn from each and every transaction. Over time, machine learning algorithms learn to recognize patterns in vendor formats and invoice structures, which improves accuracy.
The system identifies line items, tax amounts, invoice numbers, and payment terms, even when formats vary. Organizations can typically see immediate improvements in data accuracy and processing speed compared to manual processing methods.
How does traditional invoice management differ from AI- or machine learning-based approaches?
Traditional invoice management uses manual processing, with staff members receiving invoices, manually entering information into accounting systems, and routing documents for further approval. This process is time-intensive and highly prone to human error, especially considering the fact that it typically requires multiple touchpoints before final payment.
AI- or ML-based invoice management tools automate this entire workflow from receiving documents to final payment processing. The system captures information from invoices automatically, validates them against all predetermined rules, and then routes each document based on the current approval hierarchy without any need for manual intervention.
Here are the key differences between manual and automated invoice processing:
- Processing speed: Manual processing handles 5 invoices per hour; AI systems process hundreds or thousands daily
- Accuracy rates: Over 60% of invoice errors stem from manual data entry; AI systems achieve 95-99% accuracy
- Cost per invoice: Manual processing costs $12-30 per invoice; automation reduces costs to $1-5
- Approval time: Manual routing takes 10-20 days; AI workflows complete in 1-3 days
What are the biggest pain points in manual invoice processing?
Manual data entry remains the biggest pain point for 37% of accounts payable (AP) professionals. The repetitive nature of data entry as a process diverts skilled professionals from more strategic tasks. For example, finance teams often have to input invoice data manually instead of performing higher-value analysis that could improve business outcomes.
Human error rates are also a significant issue in manual invoice processing. As mentioned earlier, over 60% of invoice errors are attributed to manual data entry. The exact errors include duplicate payments, incorrect data entry, and missed early payment discounts. These errors create reconciliation challenges, which often take extra time to identify and fix.
Lack of visibility into the invoice statuses creates various bottlenecks in the approval process. Invoices can get lost in long email chains or simply sit there waiting for approval unnoticed. The absence of real-time invoice tracking is what makes things like cash flow forecasting and vendor inquiry response that much more difficult.
Compliance and audit risks are also known to increase with manual invoice processing. Unstructured filing environments are an active detriment to any attempt to maintain proper documentation trails or demonstrate compliance with financial regulations.
Why are businesses switching to AI-powered invoice solutions now?
Technological maturity has finally reached a point where AI-powered invoice solutions are capable of delivering reliable results without the need for extensive customization. By removing the need for large upfront investments, cloud-based platforms made these solutions accessible to businesses of all sizes, not just large enterprises.
Business pressure also drives a degree of urgency around digital transformation. Organizations are under greater pressure to achieve higher efficiency at lower cost. Additionally, the rise of remote work environments made the issues of paper-based processes a lot more prominent. Modern-day finance teams need solutions that can enable distributed workflows and grant real-time visibility regardless of a company’s location.
Return-on-investment (ROI) timelines have also reduced dramatically in recent years. Most businesses achieve ROI within 6–12 months after implementing AI-powered invoice solutions. The combination of reduced labor costs, fewer errors, captured discounts, and better cash flow visibility creates a strong financial case that resonates with executives.
Meanwhile, regulatory requirements are becoming more and more complex as time goes on. AI-powered invoice solutions manage to simplify compliance management to a certain degree by offering automated audit trails, standardized documentation, and real-time reporting. It’s now easy for organizations to recognize that manual processes can’t meet evolving regulatory demands without a large increase in staff.
How does AI-based invoice processing actually work?
AI invoice processing uses several technologies that are connected to each other, automating invoice handling processes from document receipt to payment approval. The system passes invoices through a sequential set of stages: data capture, extraction, validation, and routing.
Each component of such a system plays its own specific role in transforming highly unstructured invoice documents into actionable financial information that could be directly integrated with different accounting systems.
What technologies power AI invoice processing systems?
AI invoice processing combines the following four core technologies to automate the process of document handling:
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR) converts text from invoice images and PDFs into machine-readable data, enabling the system to process both digital and scanned documents.
- Machine Learning (ML) analyzes invoice patterns and improves extraction accuracy over time, learning from each processed document to handle new formats automatically.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) interprets text context and handles variations in invoice language, formatting, and terminology across different vendors and regions.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) executes repetitive tasks based on predefined rules, including data entry, document routing, and system integrations.
These technologies operate in tandem to create a highly intelligent system with many different variables. OCR captures the visual information, ML validates and categorizes it, NLP understands the context and variations of scanned data, and RPA handles workflow execution. Such integration helps systems process invoices in many different formats without the need to develop a manual template for each new invoice type.
How does AI invoice data capture work from scanned invoices, PDFs, and emails?
AI invoice processing systems are capable of receiving invoices using a number of channels, including:
- Email forwarding with dedicated inbox addresses
- Direct file upload via web portals
- Scanned documents from multifunctional devices
- Electronic data interchange connections (EDI)
The system can automatically queue incoming invoices for further processing, regardless of how they were submitted.
The AI-powered OCR converts invoice images into text by identifying specific characters, numbers, and symbols. It can even recognize text when the invoices themselves contain different fonts, layouts, or quality levels. Modern OCR engines are capable of processing both digital documents and scanned physical ones with ease.
Once the text conversion process is complete, machine learning algorithms come in, identifying and extracting specific fields from invoice data. It locates vendor names, invoice numbers, dates, line items, tax amounts, and totals by detecting recognizable patterns in document structure. Data extraction is performed automatically with no need for predefined templates for different invoice types or formats.
Extracted data is then fed directly into the fields of the accounting systems. At this stage, the system assigns general ledger codes, cost centers, and department allocations using historical patterns and pre-set business rules. Validated invoice information flows into enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms or accounting software via API connections that remove the need for manual data entry.
How does machine learning improve invoice data extraction over time?
Machine learning enables AI invoice processing systems to improve performance through continuous learning. The system begins with baseline algorithms trained on thousands of invoice examples, achieving initial accuracy rates of 85-90% which improve to 95-99% for regular vendor invoices within 6 months.
Pattern recognition drives this improvement process. As the system processes invoices from the same vendors repeatedly, it learns where specific data fields appear on each vendor's documents. That’s how it identifies consistent patterns in invoice layouts, terminology, and data placement.
When users correct extraction errors or validate invoice data, the machine learning model incorporates this feedback. The corrections teach the system to handle similar situations more accurately in future processing. Each validation strengthens the model's ability to recognize invoice variations and edge cases.
Vendor-specific learning accelerates over time. After processing 10-20 invoices from a particular vendor, the system develops reliable extraction patterns for that vendor's format. Organizations with high-volume repeat suppliers or vendors see the most dramatic accuracy improvements, reaching near-perfect extraction rates after several months of processing.
What is Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and why does it matter?
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is the technology that converts images of text into machine-readable digital data. When an invoice arrives as a scanned document or PDF image, OCR reads the visual characters and transforms them into text that computers can process and analyze.
OCR serves as the foundation for automated invoice processing. Without OCR, systems cannot extract data from paper invoices or image-based PDFs. The technology enables organizations to process invoices received in any format without requiring manual data entry from staff members.
Traditional OCR systems face limitations with varying invoice layouts, poor scan quality, or unusual fonts. These tools often require manual template configuration for each vendor format, creating maintenance overhead as vendors change their invoice designs.
Modern OCR enhanced with AI and machine learning overcomes these limitations. AI-enhanced OCR achieves impressive accuracy on varied invoice formats without template requirements. The system adapts to new layouts automatically and handles challenging scenarios, including handwritten notes, stamps, or degraded document quality.
How do AI systems learn to recognize different invoice formats?
AI invoice processing systems use template-free learning to handle diverse invoice formats without manual configuration. The system analyzes invoice structure and content patterns rather than relying on fixed templates for each vendor.
When processing a new invoice format, machine learning algorithms identify common invoice elements by analyzing document structure. The system recognizes headers, line item tables, total sections, and payment terms regardless of their position on the page. Pattern recognition allows the system to extract data from invoices it has never encountered before.
Format adaptation occurs through exposure to invoice variations:
- Single-page vs. multi-page invoices
- Digital PDFs vs. scanned paper documents
- Multiple languages and currencies
- Industry-specific terminology and layouts
- Varying levels of detail in line items
The system builds knowledge of vendor-specific patterns over time. After processing several invoices from the same vendor, the extraction accuracy for that vendor improves significantly. Organizations benefit from this learning without investing time in template creation or maintenance.
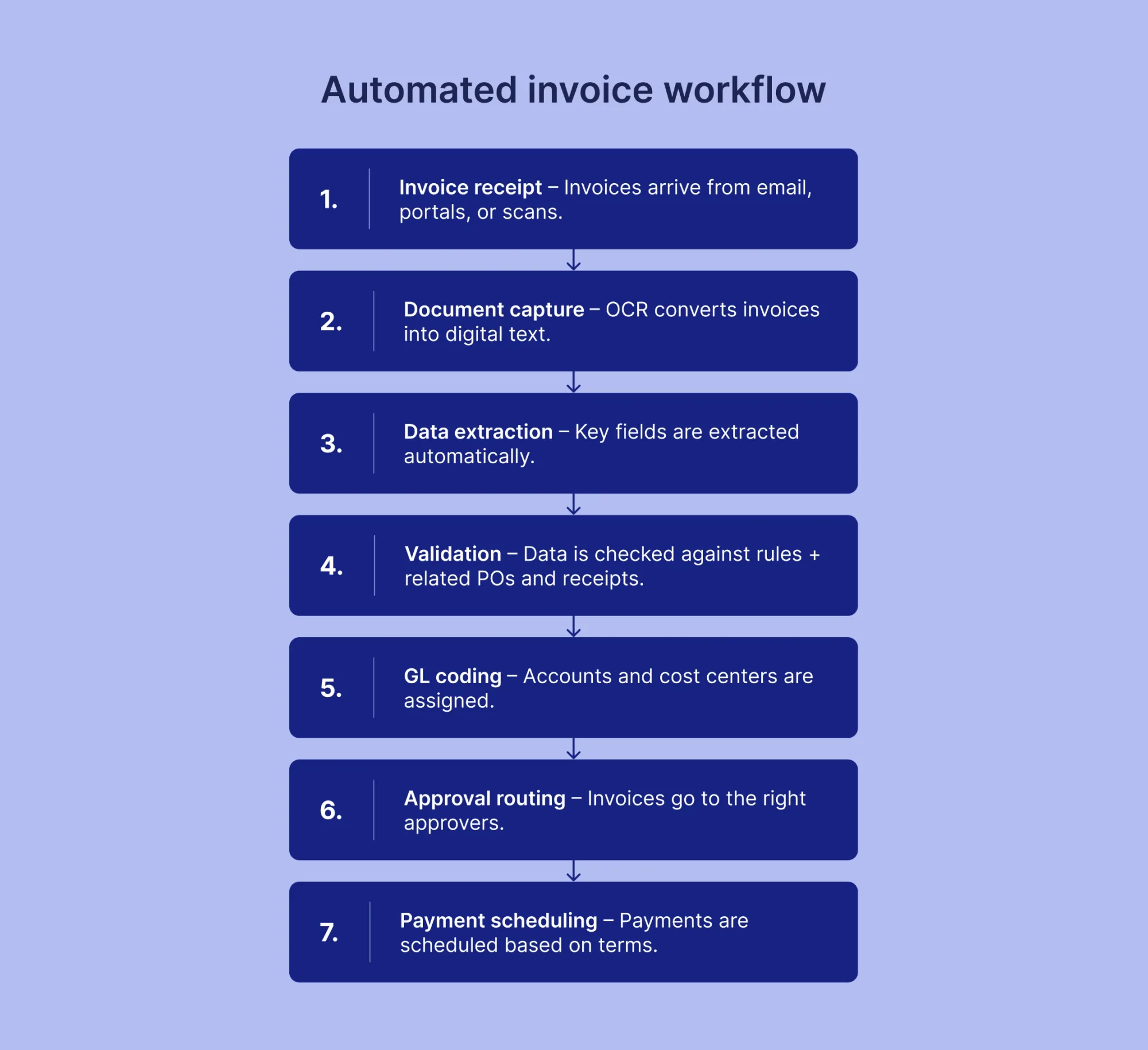
What happens to an invoice from receipt to approval in an automated system?
The automated invoice workflow progresses through seven distinct stages:
- Invoice receipt. The system receives invoices through email, portal uploads, or scanned documents. Incoming invoices enter a centralized queue regardless of submission channel.
- Document capture. OCR technology converts invoice images into digital text. The system processes both native PDFs and scanned documents within seconds.
- Data extraction. Machine learning algorithms identify and extract key fields, including vendor information, invoice number, date, line items, taxes, and total amount. Processing occurs in 1-2 seconds per document.
- Validation. The system validates extracted data against purchase orders, receipts, contracts, and business rules. Automated checks identify discrepancies, duplicates, or missing information that require attention.
- GL coding. Artificial intelligence assigns general ledger codes, cost centers, and department allocations based on historical patterns and predefined rules. The system learns coding patterns from past invoices.
- Approval routing. Invoices are automatically routed to the right approvers based on amount thresholds, departments, or vendor relationships. Approvers receive notifications through email, mobile apps, or collaboration platforms.
- Payment scheduling. Approved invoices enter the payment queue. The system schedules payments according to terms, cash flow optimization, or early payment discount opportunities.
Exception handling occurs at any stage where the system encounters low confidence scores, validation failures, or unusual patterns. These invoices are routed to AP staff for review with highlighted issues and suggested resolutions.
What are the key benefits of AI invoice processing?
AI invoice processing delivers measurable improvements across time, cost, accuracy, and financial management. Organizations implementing automation report significant operational gains within months of deployment. The benefits extend beyond simple efficiency improvements to transform accounts payable from a cost center into a strategic function that improves financial performance.
How much time can businesses save with invoice automation?
Invoice automation dramatically reduces processing time per invoice. What once required 15-20 minutes of manual work now completes in just 2-5 minutes, representing an 80% reduction in staff effort.
Organizations processing 1,000 invoices monthly save 50-80 hours per month in staff time. This freed capacity allows finance teams to shift focus from data entry to strategic activities like financial analysis, vendor relationship management, and process improvement initiatives.
Finance teams reallocate the majority of their processing time from manual data entry to strategic activities. Staff members shift focus to financial analysis, vendor relationship management, and process improvement initiatives, which generate higher value for the organization.
According to the PayStream Advisors research, companies using automated invoice processing increase productivity by 33% while reducing overall processing costs by 42%. As invoice volumes grow, the time saved allows organizations to scale without hiring more staff.
What cost reductions can you expect from automated invoice processing?
Direct processing costs decrease dramatically through automation. Organizations save on multiple fronts, including reduced labor requirements, minimized paper and storage expenses, and captured early payment discounts.
Labor cost reductions represent the largest savings category. Automated systems handle data entry, validation, and routing without manual intervention. Organizations redirect staff from repetitive tasks to higher-value work without reducing headcount.
Paper and storage costs disappear with digital processing. Organizations don’t have to pay for physical document storage, printing, postage, and filing systems. Annual savings from eliminated paper processes typically range from several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on invoice volume.
Early payment discount capture generates significant additional savings. For businesses handling 5,000 invoices a year, automation can capture savings of $30,000–$150,000 annually. The faster processing enables teams to consistently meet discount deadlines that manual processes miss.
How does AI reduce human errors in invoice management?
AI automation reduces invoice error rates from 2% in manual processes to 0.8% with automation, according to APQC research. The most advanced systems achieve error rates below 1% through continuous validation and intelligent exception handling.
Duplicate payment prevention improves dramatically with AI detection. Systems analyze invoice numbers, amounts, dates, and vendor information simultaneously to catch duplicates before payment. Organizations minimize duplicate payment incidents through automated validation.
Automated validation catches discrepancies before payment processing. Systems flag mismatched amounts, incorrect GL codes, and missing purchase order references. As a result, companies prevent costly corrections and vendor disputes, which damage business relationships.
Can invoice automation improve vendor relationships?
Automation improves vendor relationships through consistent, reliable payment practices. On-time payment rates increase from 70% to 95% when organizations implement automated processing. Vendors get paid on time, which builds trust and strengthens partnerships.
Vendor disputes decrease substantially due to improved accuracy and validation. Automated systems catch discrepancies before payment and prevent refunds, credits, and correction cycles, which strain relationships.
Real-time visibility benefits both parties. Vendors can check payment status through self-service portals rather than calling accounts payable staff. This transparency reduces inquiry volume and demonstrates organizational professionalism.
Consistent early payment positions organizations favorably during negotiations. Vendors offer better pricing, extended payment terms, or priority treatment during supply shortages to reliable customers who pay promptly.
What impact does automation have on cash flow management?
Automation accelerates invoice processing from one to two weeks down to just a few days, providing better control over payment timing. Finance teams gain visibility into upcoming obligations and can optimize payment schedules based on cash availability.
Early payment discount capture improves from 58% in manual processes to 85-95% with automation, according to the Institute of Financial Operations and Leadership research. This improvement generates substantial savings on annual spending.
Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) becomes more manageable. Systems provide real-time dashboards showing payment obligations several months forward, enabling accurate cash flow forecasting.
Predictive analytics help finance teams anticipate cash needs and identify optimal payment timing. This intelligence supports strategic decisions about working capital deployment and liquidity management.
What features should you look for in AI invoice processing software?
Selecting the right AI invoice processing platform requires careful evaluation of features that address your organization's specific needs. Modern solutions like Precoro combine automation capabilities with intuitive workflows designed for finance teams managing complex approval hierarchies and diverse vendor relationships.
The most effective platforms deliver immediate value while providing scalability for future growth. Organizations should prioritize features that address current bottlenecks, integrate seamlessly with existing systems, and maintain security standards required for financial operations.
What are the must-have features in modern invoice automation tools?
Essential features determine whether an invoice automation platform delivers promised efficiency gains:
- Intelligent data capture and extraction: OCR combined with machine learning to process invoices from any source, including email, scanned documents, and digital PDFs without manual data entry.
- Automated approval routing: Configurable workflows that route invoices to appropriate approvers based on amount thresholds, departments, cost centers, or vendor relationships.
- Three-way matching: Automatic invoice reconciliation with purchase orders and receipts to ensure accuracy before payment authorization.
- Exception management: Intelligent flagging of discrepancies, duplicates, or policy violations with clear escalation paths for items requiring human review.
- Real-time reporting and analytics: Dashboards and reports providing visibility into processing status, bottlenecks, spending patterns, and key performance metrics.
- Mobile accessibility: Approval capabilities through mobile devices, enabling timely decisions regardless of approver location.
- Audit trail maintenance: Complete documentation of all actions, approvals, and modifications to support compliance requirements and internal controls.
In Precoro, these features work together to create touchless processing for standard invoices while efficiently handling exceptions that require attention.

How important is integration with existing accounting systems?
Integration with existing accounting and ERP systems represents a critical success factor for invoice automation. Systems must connect seamlessly with platforms like QuickBooks, NetSuite, Xero, Microsoft Dynamics, and Sage to avoid creating data silos, which require manual reconciliation.
Bidirectional data synchronization ensures invoice data flows automatically into general ledgers while pulling vendor information, chart of accounts structures, and purchase order details from source systems. It prevents duplicate data entry and maintains consistency across platforms.
Poor integration creates more problems than it solves. Organizations that implement automation without proper ERP integration often end up manually transferring data between systems, which cancels out the efficiency gains automation is supposed to deliver. The integration capability should support real-time or near-real-time synchronization rather than requiring batch uploads, which delay visibility.
Evaluate integration complexity during vendor selection. Solutions with pre-built connectors for your ERP significantly reduce implementation time and ongoing maintenance compared to custom integrations.
What role does automatic data validation play?
Automatic data validation checks invoices against multiple criteria before approval, preventing errors from entering financial systems. Invoices are validated in real time, so issues are caught immediately rather than during reconciliation.
Purchase order matching compares invoice line items, quantities, and prices against authorized purchase orders. The system flags discrepancies that exceed tolerance thresholds, ensuring organizations only pay for goods and services that were ordered and received.
Duplicate detection analyzes invoice numbers, amounts, dates, and vendor information to identify potential duplicate submissions. Advanced systems recognize duplicates even when invoice numbers differ slightly, or vendors submit the same invoice through multiple channels.
Business rule validation enforces organizational policies automatically. Systems check for required approvals, spending limits, GL code accuracy, and vendor authorization status. Invoices with errors go to review rather than payment.
These validation layers provide multiple checkpoints that catch errors often missed during manual review, especially during high-volume periods when staff attention is divided.
Should your invoice software support multi-language and multi-currency processing?
Multi-language and multi-currency capabilities are essential for organizations that operate internationally or work with foreign suppliers. These features remove the complexity that would otherwise require manual handling of every international transaction.
Language processing enables systems to extract data from invoices in multiple languages without requiring separate configurations. For example, Precoro’s interface supports English, German, French, and Spanish, while its OCR can read invoices in numerous other languages, including Norwegian, Japanese, Hebrew, Swedish, Traditional Chinese, and more.
Currency handling automatically converts foreign currency amounts to the base currency using current exchange rates. Systems maintain original currency values for audit purposes while recording transactions in the organization's reporting currency.
Organizations without international operations can deprioritize these features. However, companies planning future expansion should verify that the platform supports multi-language and multi-currency processing to avoid costly system changes when business needs evolve.
What security features are essential for invoice processing systems?
Invoice processing systems handle sensitive financial data requiring robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and fraud:
- Data encryption: End-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest, protecting invoice information from interception or unauthorized access to stored data.
- Role-based access controls: Granular permissions that specify which users can view, edit, approve, or access specific invoice types, vendors, or spending categories.
- Multi-factor authentication: Additional verification beyond passwords to prevent unauthorized system access even when credentials become compromised.
- Compliance certifications: SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, and GDPR compliance demonstrating adherence to recognized security and privacy standards.
- Audit trail completeness: Immutable records of all system actions, including who added invoices, what changes were made, and when approvals were granted.
- Fraud detection algorithms: AI-powered analysis identifying unusual patterns, such as vendor information changes, invoice anomalies, or payment requests outside normal parameters.
Organizations should verify that security features meet their industry requirements and internal policies before implementation. Financial services, healthcare, and government contractors face particularly stringent security mandates that not all platforms satisfy.
How can AI handle different types of invoices and exceptions?
AI invoice processing systems handle diverse invoice formats and exceptions through flexible recognition capabilities combined with intelligent routing for items requiring human review. Modern platforms process standard invoices automatically while identifying exceptions that need attention. This hybrid approach ensures accuracy without sacrificing the speed benefits automation provides.
Can AI process invoices in various formats (PDF, email, scanned documents)?
AI systems process invoices regardless of format or submission channel. Digital PDFs, scanned paper documents, email attachments, and even smartphone photos all feed into the same processing pipeline.
Format flexibility extends to document quality variations. Systems handle low-resolution scans, skewed images, and documents with stamps or handwritten annotations. OCR technology adapts to different fonts, layouts, and paper sizes without requiring format-specific configurations.
The system automatically processes multi-page invoices by recognizing page breaks and keeping context across pages. Line items that span multiple pages are fully extracted without manual work.
Because the system accepts invoices in different formats, vendors aren’t forced into a single layout, which reduces friction in the submission process.
How does automation handle non-standard or complex invoices?
Non-standard invoices include documents with unusual layouts, mixed content types, handwritten notes, or formats the system encounters infrequently. AI systems handle these through confidence scoring and intelligent exception routing.
Confidence scoring assigns reliability ratings to extracted data. When the system extracts invoice information, it evaluates certainty levels for each field. High-confidence extractions proceed automatically while low-confidence items are flagged for human review.
The system learns from all corrections. When staff members review flagged invoices and correct extraction errors, the machine learning model incorporates this feedback. After processing several invoices from the same vendor or format type, the system can improve the extraction accuracy for similar documents later on.
Complex scenarios that require judgment are routed to human reviewers. Invoices with multiple billing entities, prorated charges, or unusual payment terms are flagged for verification, even when data extraction succeeds. This measure helps ensure financial accuracy for transactions that fall outside normal patterns.
Organizations typically see exception rates decrease over time as the system learns to handle their specific invoice variations more effectively.
What happens when the AI encounters unclear or missing information?
Systems identify unclear or missing information through validation checks applied during processing. When critical data cannot be extracted with sufficient confidence or required fields remain empty, the invoice enters an exception queue for human review.
Common triggers for manual review include:
- Illegible text or severely degraded document quality.
- Missing purchase order numbers when PO matching is required.
- Unclear or conflicting amounts where totals don’t reconcile with line item sums.
- Unrecognized vendor information that doesn’t match existing vendor master records.
- Invalid or missing tax identification numbers that are required for compliance.
Exception workflows route flagged invoices to appropriate staff members with context about the specific issue requiring attention. The system highlights problem areas and often suggests potential resolutions based on similar historical invoices.
Reviewers correct issues directly within the platform, and approved invoices return to the automated workflow for processing. This targeted intervention approach focuses human effort only on items genuinely requiring judgment while automation handles routine processing.
How are invoice discrepancies and duplicates detected automatically?
Automated discrepancy detection compares invoice data against multiple reference points to identify inconsistencies before payment authorization.
Purchase order matching identifies discrepancies between invoiced and ordered items. The system flags quantity differences, price variances exceeding tolerance thresholds, and line items appearing on invoices without corresponding purchase order entries. Organizations configure tolerance levels based on their policies, typically allowing small variances while flagging significant discrepancies.
Duplicate detection analyzes multiple criteria simultaneously rather than relying solely on invoice numbers. Systems compare vendor names, invoice amounts, dates, and line item details to identify potential duplicates. Fuzzy matching algorithms recognize duplicates even when invoice numbers contain typographical errors or vendors submit the same invoice through different channels.
Historical pattern analysis flags invoices that deviate from normal vendor behavior. Unusual amounts, unexpected payment terms, or invoice frequencies outside typical ranges trigger review. This approach catches both genuine errors and potential fraud attempts before payments are processed.
Tolerance settings balance automation efficiency with control requirements. Strict tolerances catch more discrepancies but increase exception rates, while looser tolerances enable higher straight-through processing at some risk of missed variances. Organizations adjust these settings based on their risk tolerance and vendor reliability.
Manual vs. AI‑led invoice processing (comparison)
Organizations evaluating invoice automation benefit from understanding concrete differences between manual and AI-led approaches. The following comparison table highlights key operational metrics that impact efficiency, cost, and accuracy across the invoice-to-payment lifecycle.
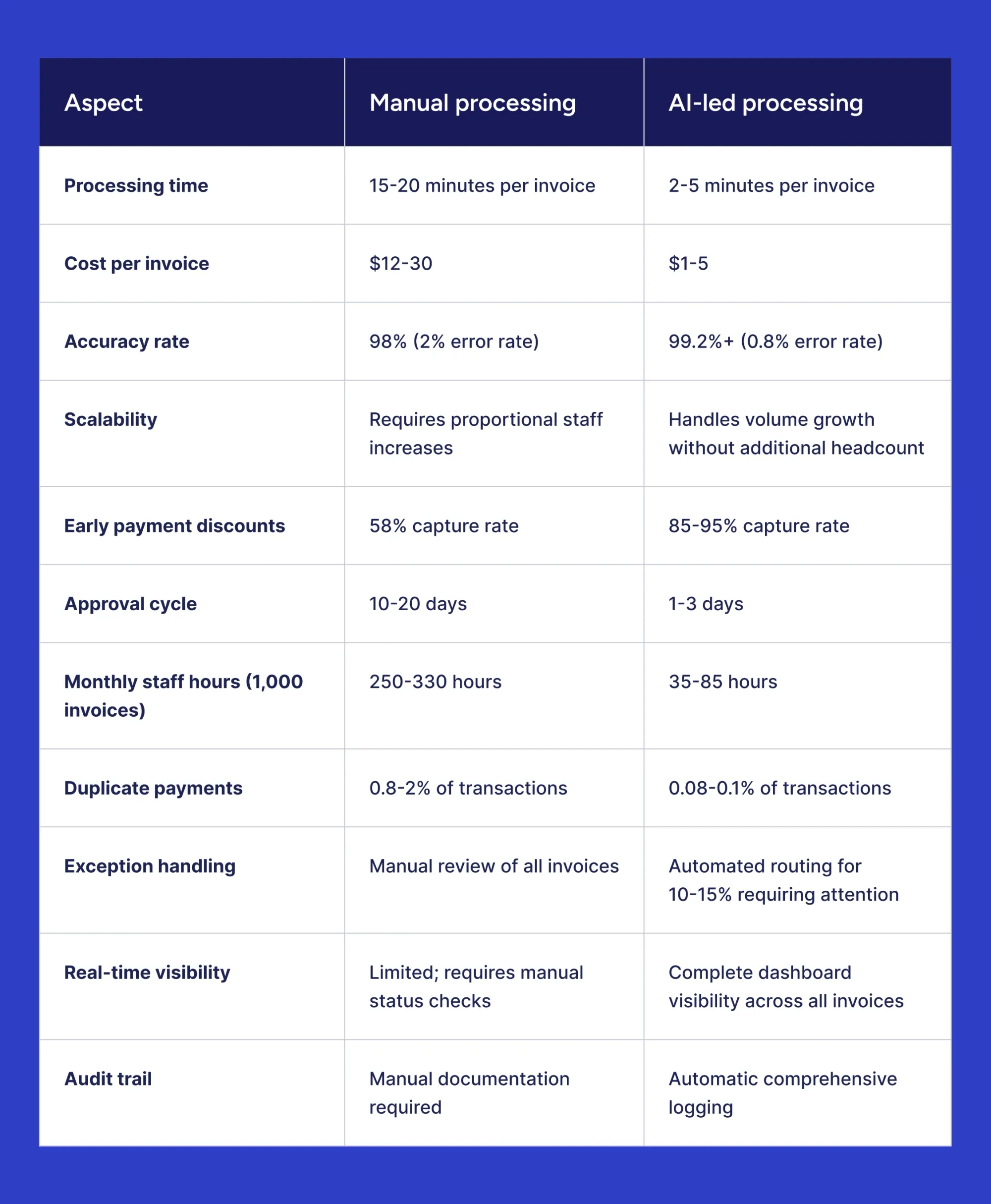
The operational differences translate directly into financial impact. Organizations processing moderate invoice volumes achieve ROI within 6-12 months through combined savings in labor costs, error reduction, and captured payment discounts. Manual processing remains viable only for very small organizations with minimal invoice volumes and no growth trajectory.
What are the implementation steps for AI invoice automation?
Successful AI invoice automation implementation follows a structured approach from initial assessment through deployment and measurement. Organizations that plan thoroughly and involve stakeholders early achieve faster time-to-value and higher user adoption rates. The implementation process typically spans several weeks to months, depending on organizational complexity and integration requirements.
How do you assess if your business is ready for invoice automation?
Several indicators signal readiness for invoice automation investment:
Invoice volume represents the primary consideration. Organizations processing 100+ invoices monthly typically achieve positive ROI from automation. Higher volumes accelerate payback periods, with businesses handling 500+ monthly invoices seeing particularly strong returns.
Current pain points justify automation priority. Frequent late payments, high error rates, lost invoices, or staff overtime dedicated to invoice processing indicate systems struggling under manual workloads. Organizations missing early payment discounts or facing vendor complaints about payment delays benefit immediately from automation.
Growth trajectory influences timing decisions. Companies experiencing rapid growth or anticipating expansion should implement automation before manual processes become overwhelmed. Scaling automated systems requires minimal additional resources compared to proportional staff increases and manual processing demands.
Process maturity affects implementation success. Organizations with documented approval workflows, strong vendor management, and clean master data implement automation more easily than those that also need to redesign processes.
What preparation is needed before implementing AI invoice processing?
Proper preparation accelerates implementation and improves outcomes:
- Clean vendor master data: Review and consolidate duplicate vendor records, verify tax identification numbers, confirm banking information, and standardize vendor naming conventions across systems.
- Document current workflows: Map existing approval hierarchies, spending thresholds, exception handling procedures, and GL coding rules to configure the automation system accurately.
- Assess integration requirements: Identify all systems requiring connections, including ERP platforms, accounting software, payment systems, and procurement tools, to plan technical integration scope.
- Establish baseline metrics: Measure current processing times, costs per invoice, error rates, and discount capture percentages to enable post-implementation ROI comparison.
- Secure stakeholder buy-in: Engage AP staff, approvers, IT teams, and finance leadership early to address concerns, gather requirements, and ensure organizational alignment.
- Define success criteria: Set specific targets for processing time reduction, cost savings, accuracy improvement, and user adoption to guide implementation priorities.
Organizations investing time in preparation typically complete implementations 30-40% faster than those beginning without proper groundwork.
How long does it typically take to deploy an AI invoice system?
Implementation timelines vary based on organizational complexity and integration requirements. Cloud-based solutions with pre-built ERP connectors typically deploy faster than on-premises systems requiring custom integration.
Standard implementation phases:
Small businesses with straightforward requirements complete implementations in 4-8 weeks. Mid-sized organizations with multiple approval workflows and complex integrations require 8-16 weeks. Large enterprises with global operations, legacy systems, or extensive customization needs may extend timelines to 12-20 weeks.
Timeline factors include ERP integration complexity, data migration volume, customization requirements, stakeholder availability for testing, and phased versus full rollout approaches. Organizations that deploy in phases, starting with high-volume vendor segments, often gain faster initial value and reduce implementation risk.
Most vendors provide project timelines during the sales process based on specific organizational requirements and technical environment assessments.
What training is required for staff to use automated invoice tools?
Modern AI invoice processing platforms such as Precoro are designed with intuitive interfaces, so most users are productive within hours, not weeks.
AP staff training covers invoice submission methods, exception handling workflows, and dashboard navigation. Training typically requires 2-4 hours through a combination of live sessions and self-paced materials. Staff members handling exceptions need additional training on resolution workflows and escalation procedures.
Approver training focuses on reviewing and approving invoices through web interfaces or mobile applications. Most approvers require only 30-60 minutes of training, given the straightforward nature of approval actions.
Administrator training addresses system configuration, user management, workflow adjustments, and reporting capabilities. Administrators typically complete 4-8 hours of training to manage ongoing system operations effectively.
Vendors provide ongoing support through help documentation, video tutorials, and technical support channels to address questions arising during daily use.
How do you measure ROI after implementation?
ROI measurement requires tracking key metrics before and after automation deployment:
Processing efficiency metrics include average time per invoice, total monthly processing hours, and invoices processed per full-time employee. Compare baseline measurements against post-implementation performance to quantify time savings.
Cost metrics track total processing costs, cost per invoice, and labor expenses allocated to invoice processing. Calculate hard dollar savings from reduced manual effort and paper-based processes.
Accuracy metrics measure error rates, duplicate payment incidents, and exception volumes. Improved accuracy translates to reduced correction costs and better vendor relationships.
Financial metrics capture early payment discount realization rates, late payment penalty avoidance, and days payable outstanding. These directly impact cash flow and bottom-line profitability.
Adoption metrics track system usage rates, straight-through processing percentages, and user satisfaction scores to ensure the solution delivers intended value.
Most organizations see measurable improvements within 60-90 days of deployment, with full ROI typically realized within 6-12 months as previously established.
What challenges might you face in machine learning-based AI processing?
Organizations encounter predictable challenges during invoice automation adoption. Most obstacles stem from technical integration complexity, organizational change management, or transition period concerns rather than fundamental technology limitations. Understanding common challenges and mitigation strategies enables smoother implementations and faster value realization.
What are the common obstacles during invoice automation adoption?
Several common challenges surface frequently during implementation:
- Data quality issues
- Integration complexity
- Process inconsistencies
- Vendor compliance
- Unrealistic expectations
Data quality issues in existing systems complicate automation deployment. Duplicate vendor records, inconsistent GL code usage, and incomplete vendor information require cleanup before automation delivers full benefits. Organizations with poor master data quality spend additional time during implementation addressing these foundational issues.
Integration complexity varies significantly based on existing technology infrastructure. Modern cloud-based systems typically offer straightforward integration paths, while legacy systems may require custom development work. Integration challenges extend timelines and increase implementation costs when not properly scoped during vendor selection.
Process inconsistencies across departments or locations create configuration challenges. Organizations that lack standardized approval workflows or spending policies must establish consistency before automation can enforce rules effectively.
Vendor compliance with submission requirements takes time to achieve. Vendors accustomed to multiple submission channels may resist change. Organizations need patience and clear communication to guide them toward preferred submission methods.
Unrealistic expectations about automation capabilities lead to disappointment. Systems require learning periods and cannot handle every edge case without human intervention initially.
How do you handle resistance to change from your team?
Resistance to automation typically stems from job security concerns or comfort with familiar processes. Addressing resistance requires transparent communication and demonstrated value.
Early involvement of AP staff in vendor selection and implementation planning reduces resistance. Staff members who participate in requirements gathering and testing feel ownership over the solution rather than viewing it as something imposed upon them.
Clear communication about role evolution addresses job security fears. Emphasize how automation cuts tedious data entry while enabling staff to focus on exception resolution, vendor procurement, and process improvement. After automation, organizations rarely reduce headcount; instead, they redeploy staff to higher-value activities.
Quick wins build confidence in the new system. Start automation with straightforward, high-volume invoice types, which demonstrate clear benefits. Success with initial use cases creates momentum for broader adoption. Adequate training and support ensure staff feel competent using new tools. Ongoing access to vendor support and internal champions helps staff navigate challenges during the transition period.
What if your invoices are too complex or varied for automation?
Automation often seems more complex than it really is. Modern AI systems can handle a wide range of invoice formats and content without extensive setup.
Phased implementation addresses real complexity concerns. Organizations first automate simple invoices from high-volume vendors, keeping manual processing for complex exceptions. This approach delivers immediate value and allows the system to learn organizational patterns over time.
The system becomes more accurate as it encounters different invoice variations. After repeatedly processing invoices from the same vendors, the extraction accuracy for those formats improves significantly. Many organizations find that invoices initially considered “too complex” can be fully automated within months.
Hybrid models work effectively for genuinely exceptional invoices. Organizations automate the majority of their invoice volume while maintaining manual processing for unusual transactions. This approach captures most automation benefits without forcing inappropriate use cases.
The key question isn’t whether every invoice can be automated immediately, but whether the volume is high enough to justify the investment. Organizations that handle large numbers of standard invoices benefit even if complex exceptions are still processed manually.
How do you ensure data accuracy during the transition period?
Transition periods require enhanced monitoring and validation to maintain accuracy while building confidence in automated processes.
Parallel processing during the initial weeks provides a safety net. Organizations run both manual and automated processing for the same invoices, comparing results to verify system accuracy before fully committing to automation.
During rollout, apply enhanced review protocols. Increase sampling rates for automated invoice reviews initially, then gradually reduce oversight as confidence builds. This staged approach catches issues early while avoiding permanent inefficiency.
Clear escalation paths ensure staff know how to handle uncertain situations. Document when to override system suggestions, how to report extraction errors, and which scenarios require management review.
Validation checkpoints at critical stages prevent errors from propagating. Implement approval requirements for invoices above certain thresholds or from new vendors, regardless of automation confidence levels.
Most organizations achieve comfort with automated accuracy within 30-60 days of deployment, at which point monitoring returns to standard exception-based oversight.
Which industries benefit most from AI invoice processing?
AI invoice processing delivers value across industries, though specific benefits vary based on operational characteristics and pain points. Organizations in high-volume sectors, complex supply chain environments, or compliance-intensive industries see particularly strong returns from automation investments. The following examples illustrate how different verticals leverage automation to address industry-specific challenges.
How does invoice automation transform financial services companies?
Financial services organizations operate under stringent regulatory requirements demanding complete audit trails and documentation accuracy. Invoice processing automation provides the controls and transparency these regulations require while improving operational efficiency.
Compliance capabilities built into automation platforms maintain comprehensive records of all invoice actions, approvals, and modifications. Systems generate audit trails automatically, freeing staff from time-consuming manual documentation during regulatory reviews.
Multi-entity processing complexity characterizes financial services operations. Financial services operations often involve multiple subsidiaries, divisions, or legal entities, creating complexity in invoice processing. Organizations need systems that route approvals accurately and preserve separation between business units.
High invoice volumes combined with accuracy requirements make financial services ideal candidates for automation. Processing costs decrease substantially while maintaining the precision and documentation rigor that compliance mandates require. The combination of efficiency gains and reduced compliance risk delivers compelling value for regulated entities.
Why is AI invoice processing crucial for retail and e-commerce businesses?
Retail and e-commerce operations face unique invoice processing challenges that stem from volume variability and vendor diversity:
- Seasonal volume spikes during peak shopping periods overwhelm manual processing capabilities, creating payment delays that strain vendor relationships during critical periods.
- Large vendor bases with hundreds or thousands of suppliers generate invoices in countless formats, making manual processing inconsistent and error-prone.
- Thin profit margins require operational efficiency across all functions, with invoice processing cost reductions directly improving bottom-line profitability.
- Rapid inventory turnover demands fast payment cycles to maintain supplier relationships and ensure product availability during high-demand periods.
Automation enables retail organizations to scale processing capacity instantly during peak seasons without hiring temporary staff. The system handles vendor format diversity automatically, processing invoices consistently regardless of the submission format. Cost reductions from automation help protect margins in an increasingly competitive retail environment.
E-commerce businesses particularly benefit from the speed automation provides. Fast-growing online retailers add vendors rapidly as they expand product catalogs, and automation accommodates this growth without proportional increases in AP staff.
What advantages does automation offer to manufacturing firms?
Manufacturing operations involve complex supply chains and procurement processes that create specific automation advantages:
- Multi-location operations with plants in different regions require centralized invoice processing visibility while maintaining location-specific approval workflows.
- Complex supply chains that involve raw materials, components, and services from numerous vendors generate high invoice volumes requiring efficient processing.
- Purchase order-based procurement means most manufacturing invoices can leverage three-way matching automation, delivering particularly high straight-through processing rates.
- Material cost tracking for job costing and inventory valuation relies on accurate invoice data, captured and coded correctly for financial reporting.
Manufacturing firms typically achieve some of the highest automation success rates due to structured procurement processes and PO-based purchasing prevalence. Three-way matching automation handles the majority of invoices without manual intervention, freeing AP staff to focus on exceptions and vendor management.
The ability to track costs accurately by project, product line, or manufacturing location improves financial visibility. Automated GL coding based on purchase order data ensures costs are allocated correctly without manual coding decisions that introduce errors.
How do professional services firms leverage AI for invoice management?
Professional services organizations face different invoice processing challenges than high-volume industries, but still benefit significantly from automation.
Project-based billing complexity requires tracking invoices against specific client engagements, matters, or projects. Automation systems code invoices to appropriate projects automatically based on vendor relationships and historical patterns, improving cost tracking accuracy for client billing and profitability analysis.
Client reimbursement management represents a significant pain point for professional services firms. Automation systematically maintains the detailed records needed to track reimbursable vendor expenses, allocate them to client projects, and ensure proper billing.
Time-sensitive payment needs characterize professional services operations. Vendors who provide specialized expertise or temporary staff need prompt payment to support client service. Automation speeds up approval cycles, ensuring payments are made on time.
While professional services firms process fewer invoices than retail or manufacturing operations, the complexity and importance of accurate project cost tracking justify automation investments. Better financial visibility into project profitability often provides value that exceeds the direct savings from reduced processing costs.
Evaluating & selecting AI invoice processing software
Vendor selection requires evaluation beyond feature checklists. The right platform combines strong technical capabilities with reliable implementation support and transparent pricing models. Organizations should assess multiple vendors through structured evaluation processes before selecting an implementation partner.
Critical evaluation criteria include:
- Proven track record with organizations in your industry and size category, verified through customer references and validated case studies.
- Implementation methodology with dedicated support resources, realistic timeline estimates, and structured onboarding processes that minimize business disruption.
- Pricing transparency covering all costs, including licensing, implementation fees, ongoing support, and transaction-based charges to enable accurate total cost of ownership calculations.
- Integration capabilities with your specific ERP and accounting systems, preferably through pre-built connectors rather than custom development.
- Scalability to accommodate business growth and increased invoice volumes without requiring platform migration or significant reconfiguration.
- Vendor financial stability and product roadmap demonstrating ongoing investment in platform development and long-term viability.
- Trial or proof-of-concept availability allows testing with your actual invoices before full commitment.
Request demonstrations with your invoice samples rather than vendor-prepared examples. Evaluate extraction accuracy, exception handling, and workflow configuration using real documents that reflect your processing complexity. Involve AP staff and approvers in vendor demonstrations to gather feedback from actual system users.
Select vendors offering phased implementation approaches, which deliver value incrementally rather than requiring complete process transformation all at once.
What does the future hold for AI invoice processing?
AI invoice processing technology is evolving quickly, with new capabilities promising even greater automation and intelligence. Current systems already deliver significant value, but the next generation will offer more autonomy, predictive features, and seamless integration across financial ecosystems.
What emerging trends are shaping invoice automation technology?
Several technological developments are influencing invoice automation evolution:
Generative AI explains why items are flagged and suggests solutions based on similar past cases. Today’s platforms go beyond identifying issues to provide thoughtful, reasoned recommendations.
Autonomous processing capabilities expand as systems gain confidence in handling edge cases. Platforms make independent decisions on low-risk exceptions, which previously required human review, further reducing manual intervention requirements.
Predictive analytics enable proactive cash flow management by forecasting payment obligations, identifying optimal payment timing, and recommending working capital strategies based on historical patterns and current business conditions.
Natural language interfaces allow users to query systems conversationally, generate custom reports through simple requests, and configure workflows without technical expertise.

How will AI invoice processing evolve in the next 5 years?
The next evolution phase focuses on increased intelligence and ecosystem integration rather than fundamental technological shifts.
Processing autonomy will increase substantially. Systems currently handling 80-90% of invoices automatically will reach 95%+ touchless rates as confidence scoring improves and edge case handling becomes more sophisticated.
Integration ecosystems will expand beyond accounting systems to encompass procurement platforms, payment networks, vendor portals, and banking systems. This connectivity will enable end-to-end automation from purchase requisition through payment reconciliation.
Adaptive learning will speed up, with systems needing very little training and automatically adjusting to organizational changes. New vendor formats can be processed accurately after just one or two examples, instead of requiring dozens of invoices to recognize patterns.
Collaborative intelligence will allow invoice systems to exchange data with spend, budgeting, and forecasting tools, providing a complete view of financial performance.
How will blockchain impact future invoice management?
Blockchain has the potential to verify invoices and automate payments using smart contracts, though mainstream adoption remains years away.
Smart contracts could trigger payments automatically when contract conditions are met, removing approvals for routine transactions. Blockchain-based invoice verification could lower fraud risk and simplify vendor onboarding.
Blockchain adoption still faces major challenges, including low vendor participation, complex integration with existing systems, and regulatory uncertainty. Organizations should keep an eye on blockchain developments, but focus their implementation efforts on proven technologies that deliver value now.
Blockchain may eventually play a supporting role in invoice ecosystems rather than replacing current automation approaches entirely.
Best practices for AI invoice processing
Successful invoice automation requires ongoing attention to system optimization and organizational adoption. The following best practices help organizations maximize automation value and maintain high performance over time.
Implementation and operation best practices:
- Start with high-volume vendors to deliver immediate impact while allowing time for the system to learn patterns from your most frequent invoice sources.
- Keep master data clean with regular vendor file reviews, duplicate removal, and standardized naming conventions to improve matching accuracy.
- Set appropriate tolerance thresholds balancing automation efficiency with control requirements based on organizational risk tolerance and vendor reliability.
- Monitor exception patterns regularly to identify recurring issues requiring workflow adjustments, additional vendor training, or system configuration refinements.
- Involve stakeholders early in selection, configuration, and testing phases to ensure buy-in and gather practical requirements from actual system users.
- Document baseline metrics before implementation to enable accurate ROI measurement and demonstrate value to organizational leadership.
- Provide adequate training for all user groups, including AP staff, approvers, and administrators, with ongoing access to support resources.
- Establish vendor communication about preferred invoice submission methods and required information to improve initial processing success rates.
- Review and optimize workflows quarterly based on performance data, user feedback, and changing business requirements.
- Plan for continuous improvement instead of treating implementation as a one-time project, and take advantage of system learning capabilities and new features.
Organizations treating automation as an evolving capability rather than a static solution achieve superior long-term results and sustained efficiency gains.
Frequently asked questions
Yes, AI-powered spend analytics identify vendor consolidation opportunities by analyzing purchasing patterns across the organization. The systems detect multiple vendors providing similar goods or services, highlight spending fragmentation, and quantify potential savings from consolidated purchasing agreements. These insights enable procurement teams to negotiate better terms with fewer vendors while maintaining service quality.
AI invoice processing handles non-PO invoices effectively through GL coding rules, approval workflows, and historical pattern matching. Systems assign general ledger codes based on vendor relationships and past invoices, then route for approval according to amount thresholds and department rules. While PO-based invoices achieve higher straight-through processing rates, non-PO invoices still benefit substantially from automated data capture and workflow routing.
Real-world AI invoice extraction typically achieves 95-99% accuracy on standard invoices, with performance varying based on document quality and format consistency. Invoice quality (resolution, clarity, layout standardization) represents the primary accuracy factor, followed by vendor format consistency and system training on specific document types. Accuracy improves continuously as systems process more invoices from regular vendors and learn organizational patterns.
AI invoice automation significantly improves audit readiness through comprehensive, automated documentation of all invoice activities. Systems maintain complete audit trails showing who approved invoices, when changes were made, and why exceptions were flagged without requiring manual record-keeping. This automatic documentation reduces audit preparation time by 40-60 hours annually while providing auditors with the detailed transaction histories that compliance requirements mandate.
Turn AI invoice processing into daily efficiency. Book a Precoro demo.